Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * ▲ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Oct 2022

Guidelines for the reliable use of high throughput sequencing technologies to detect plant pathogens and pestsS. Massart, I. Adams, M. Al Rwahnih, S. Baeyen, G. J. Bilodeau, A. G. Blouin, N. Boonham, T. Candresse, A. Chandelier, K. De Jonghe, A. Fox, Y.Z.A. Gaafar, P. Gentit, A. Haegeman, W. Ho, O. Hurtado-Gonzales, W. Jonkers, J. Kreuze, D. Kutjnak, B. B. Landa, M. Liu, F. Maclot, M. Malapi-Wight, H. J. Maree, F. Martoni, N. Mehle, A. Minafra, D. Mollov, A. G. Moreira, M. Nakhla, F. Petter, A.M. Piper, J. P. Ponchart, R. Rae, B. Remenant, Y. Rivera, B. Rodoni, M. Botermans, J.W. Roenhorst, J. Rollin , ... https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7142136High-throughput sequencing for the diagnostic of plant pathologies and identification of pests: recommendations and challengesRecommended by Olivier Schumpp based on reviews by Denise Altenbach and David RoquisHigh-throughput sequencing (HTS) has revealed an incredible diversity of microorganisms in ecosystems and is also changing the monitoring of macroorganism biodiversity (Deiner et al. 2017; Piper et al. 2019). The diagnostic of plant pathogens and the identification of pests is gradually integrating the use of these techniques, but there are still obstacles. Most of them are related to the reliability of these analyses, which have long been considered insufficient because of their dependence on a succession of sophisticated operations involving parameters that are sometimes difficult to adapt to complex matrices or certain diagnostic contexts. The need to validate HTS approaches is gradually being highlighted in recent work but remains poorly documented (Bester et al. 2022). In this paper, a large community of experts presents and discusses the key steps for optimal control of HTS performance and reliability in a diagnostic context (Massart et al. 2022). It also addresses the issue of costs. The article provides recommendations that closely combine the quality control requirements commonly used in conventional diagnostics with newer or HTS-specific control elements and concepts that are not yet widely used. It discusses the value of these for the use of the various techniques currently covered by the terms "High Throughput Sequencing" in diagnostic activities. The elements presented are intended to limit false positive or false negative results but will also optimise the interpretation of contentious results close to the limits of analytical sensitivity or unexpected results, both of which appear to be frequent when using HTS. Furthermore, the need for risk analysis, verification and validation of methods is well illustrated with numerous examples for each of the steps considered crucial to ensure reliable use of HTS. The clear contextualisation of the proposals made by the authors complements and clarifies the need for user expertise according to the experimental objectives. Some unanswered questions that will require further development and validation are also presented. This article should benefit a large audience including researchers with some level of expertise in HTS but unfamiliar with the recent concepts of controls common in the diagnostic world as well as scientists with strong diagnostic expertise but less at ease with the numerous and complex procedures associated with HTS. References Bester R, Steyn C, Breytenbach JHJ, de Bruyn R, Cook G, Maree HJ (2022) Reproducibility and Sensitivity of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS)-Based Detection of Citrus Tristeza Virus and Three Citrus Viroids. Plants, 11, 1939. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11151939 Deiner K, Bik HM, Mächler E, Seymour M, Lacoursière-Roussel A, Altermatt F, Creer S, Bista I, Lodge DM, de Vere N, Pfrender ME, Bernatchez L (2017) Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Molecular Ecology, 26, 5872–5895. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14350 Massart, S et al. (2022) Guidelines for the reliable use of high throughput sequencing technologies to detect plant pathogens and pests. Zenodo, 6637519, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6637519 Piper AM, Batovska J, Cogan NOI, Weiss J, Cunningham JP, Rodoni BC, Blacket MJ (2019) Prospects and challenges of implementing DNA metabarcoding for high-throughput insect surveillance. GigaScience, 8, giz092. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giz092 | Guidelines for the reliable use of high throughput sequencing technologies to detect plant pathogens and pests | S. Massart, I. Adams, M. Al Rwahnih, S. Baeyen, G. J. Bilodeau, A. G. Blouin, N. Boonham, T. Candresse, A. Chandelier, K. De Jonghe, A. Fox, Y.Z.A. Gaafar, P. Gentit, A. Haegeman, W. Ho, O. Hurtado-Gonzales, W. Jonkers, J. Kreuze, D. Kutjnak, B. B... | <p style="text-align: justify;">High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have the potential to become one of the most significant advances in molecular diagnostics. Their use by researchers to detect and characterize plant pathogens and pests... |  | Diagnosis, Pest management, Phytopathology, Plant diseases | Olivier Schumpp | 2022-06-13 11:26:18 | View | |
08 Dec 2022
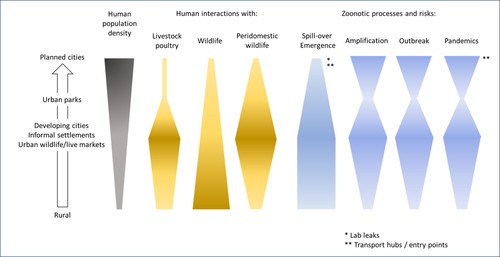
Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystemsDobigny, G. & Morand, S. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776Zoonotic emergence and the overlooked case of citiesRecommended by Etienne Waleckx based on reviews by Eric Dumonteil, Nicole L. Gottdenker and 1 anonymous reviewerZoonotic pathogens, those transmitted from animals to humans, constitute a major public health risk with high associated global economic costs. Diseases associated with these pathogens represent more than 60% of emerging infectious diseases and predominantly originate in wildlife (1). Over the last decades, the emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic pathogens have led to an increasing number of epidemics, as illustrated by the current Covid-19 pandemic. There is ample evidence that human impact on native ecosystems such as deforestation, agricultural development, and urbanization, is linked to spillover of pathogens from animals to humans (2). However, research and calls to action have mainly focused on the importance of surveillance and prevention of zoonotic emergences along landscape interfaces, with special emphasis on tropical forests and agroecosystems, and studies and reviews pointing out the zoonotic risk associated with cities are scarce. Additionally, cities are sometimes wrongly seen as one homogeneous ecosystem, almost exclusively human, with a Northern hemisphere-biased perception of what a city is, which fails to take into account the ecological and socio-economic diversities that can constitute an urban area. Here, Dobigny and Morand (3) aim to draw attention to the importance of urban ecosystems in zoonotic risk and advocate that further attention should be paid to urban, peri-urban and suburban areas. In this well-organized and well-documented review, the authors show, using updated literature, that cities are places where massive contacts occur between wildlife, domestic animals, and human inhabitants (thus constituting spillover opportunities), and that it is even likely that human and wildlife contact in urban centers is more prevalent than in wild areas, perhaps contrary to intuition. Indeed, cities currently constitute the most important environment of human life and are places for millions of close interactions between humans and animals, including pets and domestic animals, wild animals through the intrusion of wild urban-adapted species (e.g., some bat, rodent, or bird species among others), manipulation and consumption of wildlife meat, and the existence of wildlife meat markets, which all constitute a major risk for zoonotic spillover. In cities, lab escapees of zoonotic pathogens also exist, and trends of adaptation to urban ecological conditions of many vectors of primary health importance is also a concern. The authors further argue that cities are predominant places for both epidemic amplification of human-human transmitted pathogens, because they are places with high human densities and population growth, and for dissemination of reservoirs, vectors and pathogens, as they are transport hubs. Dobigny & Morand further predict, likely correctly, that cities may be important places for pathogen evolution. Finally, they propose actions and recommendations to limit the risk of zoonotic spillover events from urban ecosystems and future directions for research aiming at assessing this risk. The reviewers found the manuscript well-organized and presented, timely, and bringing novel contributions to the field of zoonotic emergence. I strongly recommend this article, which should benefit a large audience, particularly in the context of the current Covid-19 pandemics and the ongoing One Health initiatives aiming at preventing future zoonotic disease emergence (4). References (1) Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451, 990–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06536 (2) White RJ, Razgour O (2020) Emerging zoonotic diseases originating in mammals: a systematic review of effects of anthropogenic land-use change. Mammal Review, 50, 336–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/mam.12201 (3) Dobigny G, Morand S (2022) Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems. Zenodo, 6444776, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776 (4) Morand S, Lajaunie C (2021) Biodiversity and COVID-19: A report and a long road ahead to avoid another pandemic. One Earth, 4, 920–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.06.007 | Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems | Dobigny, G. & Morand, S. | <p style="text-align: justify;">Zoonotic emergence requires spillover from animals to humans, hence animal-human interactions. A lot has been emphasized on human intrusion into wild habitats (e.g., deforestation, hunting) and the development of ag... |  | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, One Health, Zoonoses | Etienne Waleckx | 2022-04-11 11:39:11 | View | |
07 Feb 2023
Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populationsMarie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084Unveiling the complex interactions between members of gut microbiomes: a significant advance provided by an exhaustive study of wild bank volesRecommended by Thomas Pollet based on reviews by Jason Anders and 1 anonymous reviewerThe gut of vertebrates is a host for hundreds or thousands of different species of microorganisms named the gut microbiome. This latter may differ greatly in natural environments between individuals, populations and species (1). The vertebrate gut microbiome plays key roles in host fitness through functions including nutrient acquisition, immunity and defense against infectious agents. While bank voles are small mammals potentially reservoirs of a large number of infectious agents, questions about the links between their gut microbiome and the presence of pathogens are scarcely addressed. In this study, Bouilloud et al. (2) used complementary analyses of community and microbial ecology to (i) assess the variability of gut bacteriome diversity and composition in wild populations of the bank vole Myodes glareolus collected in four different sites in Eastern France and (ii) evaluate the three-way interactions between the gut bacteriota, the gastro-intestinal helminths and pathogenic bacteria detected in the spleen. Authors identified important variations of the gut bacteriota composition and diversity among bank voles mainly explained by sampling localities. They found positive correlations between the specific richness of both the gut bacteria and the helminth community, as well as between the composition of these two communities, even when accounting for the influence of geographical distance. The helminths Aonchotheca murissylvatici, Heligmosomum mixtum and the bacteria Bartonella sp were the main taxa associated with the whole gut bacteria composition. Besides, changes in relative abundance of particular gut bacterial taxa were specifically associated with other helminths (Mastophorus muris, Catenotaenia henttoneni, Paranoplocephala omphalodes and Trichuris arvicolae) or pathogenic bacteria. Infections with Neoehrlichia mikurensis, Orientia sp, Rickettsia sp and P. omphalodes were especially associated with lower relative abundance of members of the family Erysipelotrichaceae (Firmicutes), while coinfections with higher number of bacterial infections were associated with lower relative abundance of members of the Bacteroidales family (Bacteroidetes). As pointed out by both reviewers, this study represents a significant advance in the field. I would like to commend the authors for this enormous work. The amount of data, analyses and results is considerable which has sometimes complicated the understanding of the story at the beginning of the evaluation process. Thanks to constructive scientific interactions with both reviewers through the two rounds of evaluation, the authors have efficiently addressed the reviewer's concerns and improved the manuscript, making this great story easier to read. The innovative results of this study emphasize the complex interlinkages between gut bacteriome and infections in wild animal populations and I strongly recommend this article for publication In Peer Community Infections. References (1) Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Sklar J, Jiang L, Natarajan L, Knight R, Belkaid Y (2020) Host variables confound gut microbiota studies of human disease. Nature, 587, 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2881-9 (2) Bouilloud M, Galan M, Dubois A, Diagne C, Marianneau P, Roche B, Charbonnel N (2023) Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations. biorxiv, 2022.05.23.493084, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084 | Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations | Marie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel | <p>Background</p> <p>Despite its central role in host fitness, the gut microbiota may differ greatly between individuals. This variability is often mediated by environmental or host factors such as diet, genetics, and infections. Recently, a part... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Reservoirs, Zoonoses | Thomas Pollet | 2022-05-25 10:13:23 | View | ||
16 Jul 2024
Diverse fox circovirus (Circovirus canine) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (Canis lupus) from the Northwest Territories, CanadaMarta Canuti, Abigail V.L. King, Giovanni Franzo, H. Dean Cluff, Lars E. Larsen, Heather Fenton, Suzanne C. Dufour, Andrew S. Lang https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.08.584028Wild canine viruses in the news. Better understanding multi-host transmission by adopting a disease ecology species community-based approachRecommended by Jean-Francois Guégan based on reviews by Arvind Varsani and 1 anonymous reviewerAccording to the international animal health authority, i.e., the World Organization on Animal Health (WOAH, former OIE), circoviruses are part of the Circoviridae family, which only includes 2 genera Circovirus and Cyclovirus, and infect swine, canine, ursid, viverrid, felid, pinniped, herpestid, mustelid, and several avian species (WOAH 2021). They are small (12–27 nm), non-enveloped, circular, single-stranded DNA viruses, viral replication is nuclear, and wild and domestic birds and mammals could serve as natural hosts. If most infections caused by circoviruses are subclinical in both wild and domestic species, they can be responsible for severe diseases in the commercial pig industry due to the Porcine circovirus-2 (PCV-2). These viruses can constitute a threat to wildlife, and cause their hosts to become immunocompromised, and animals often present with secondary coinfections. Canine circoviruses (CanineCV) harbour a worldwide distribution in dogs, and is the sole member of the viral genus to infect canines. They can be detected in wild carnivores, such as wolves, badgers, foxes and jackals, which indicates an ability for cross-species transmission between wildlife and domestic dogs. However, fox circovirus (FoCV), a distinct lineage of CanineCV, has been identified exclusively in wild canids (foxes and wolves) and not in dogs in Europe and North America, where it can cause in red foxes meningoencephalitis and other central nervous system signs. In their article, Canuti et al. (2024) investigate the presence, distribution and ecology of CanineCV in grey wolf specimens from the Northwest Territories, Canada. CanineCV occurrence appears to be relatively high with 45.3% positive specimens and parvoviral superinfections observed. The authors identify a high CanineCV genetic diversity among the investigated grey wolf specimens, and exacerbated by viral recombination. Phylogenetic analysis reveals the existence of 4 lineages, within each of them strains segregate by geography and not by host origin. This observed geographic segregation is interpreted as being due to the absence of exchange flows between grey wolf host subpopulations. Due to the paucity of knowledge on these circoviruses in wildlife and at the interface between wild and domestic animals, the authors discuss the plausible role of wolves as natural host reservoirs for disease transmission due to long-lasting virus-host coevolution. They are also conscious that additional maintenance hosts could exist in the wild, claiming for further studies to decipher fox circovirus disease ecology and transmission dynamics. This study underlines the importance of better understanding the transmission ecology and evolution of these Canine circoviruses, and I can only agree. Xiao et al. (2023), a research not referred to in the present work, evidenced CanineCV infection in cats in China, and obtained the first whole genome of cat-derived CanineCV. This emphasizes the importance of monitoring additional animal species and locations in the world to clarify disease ecology and transmission dynamics. A broader sampling of a wide range of animal species in different parts of the world using a species community-based approach is the key to understanding these CanineCV infections. References Marta CANUTI, Abigail V.L. KING, Giovanni FRANZO, H. Dean CLUFF, Lars E. LARSEN, Heather FENTON, Suzanne C. DUFOUR, Andrew S. LANG. 2024. Diverse fox circovirus (Circovirus canine) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (Canis lupus) from the Northwest Territories, Canada. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.08.584028 World Organization on Animal Health. 2021. Circoviruses. https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/05/circoviruses-infection-with.pdf [consulted on July 9th, 2024]. Xiangyu XIAO, Yan CHAO LI, Feng PEI XU, Xiangpi HAO, Shoujun LI, Pei ZHOU. 2023. Canine circovirus among dogs and cats in China: first identification in cats. Front. Microbiol. 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1252272 | Diverse fox circovirus (*Circovirus canine*) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (*Canis lupus*) from the Northwest Territories, Canada | Marta Canuti, Abigail V.L. King, Giovanni Franzo, H. Dean Cluff, Lars E. Larsen, Heather Fenton, Suzanne C. Dufour, Andrew S. Lang | <p style="text-align: justify;">Canine circoviruses (CanineCV) have a worldwide distribution in dogs and are occasionally detected in wild carnivorans, indicating their ability for cross-species transmission. However, fox circovirus, a lineage of ... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Epidemiology, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Reservoirs, Taxonomy of hosts, infec... | Jean-Francois Guégan | Martine Peeters, Arvind Varsani | 2024-03-09 09:04:29 | View | |
19 Feb 2024
Population genetics of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the diseaseMoise S. Kagbadouno, Modou Séré, Adeline Ségard, Abdoulaye Dansy Camara, Mamadou Camara, Bruno Bucheton, Jean-Mathieu Bart, Fabrice Courtin, Thierry de Meeûs, Sophie Ravel https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.25.550445Reaching the last miles for transmission interruption of sleeping sickness in Guinea: follow-up of achievements and policy making using microsatellites-based population geneticsRecommended by Hugues Nana Djeunga based on reviews by Fabien HALKETT and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Fabien HALKETT and 2 anonymous reviewers
Thanks to the coordinated and sustained efforts of national control programs, the World Health Organization (WHO), bilateral cooperation and nongovernmental organizations, the incidence of Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), better known as sleeping sickness, has drastically decreased during the last two decades (WHO, 2023a). Indeed, between 1999 and 2022, the reported number of new cases of the chronic form of sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense) fell by 97% (from 27 862 to 799), and the number of newly reported cases of the acute form of HAT (Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense) fell by 94% (from 619 to 38) (WHO, 2023b). These encouraging trends led the WHO to target this debilitating and highly fatal (if untreated) vector-borne parasitic disease for elimination as a public health problem by 2020, and for interruption of transmission (zero case) by 2030 (WHO, 2021, WHO, 2023a). However, the disease is persisting in many foci, and even some cases of resurgence have been documented after unfortunate events such as war or pandemics (Moore et al., 1999; Sah et al., 2023. Simarro et al). Although effective control measures, diagnosis and treatment are complex and require specific skills (WHO, 2023), especially in a context which animal reservoirs, including hidden reservoirs, can contribute to the maintenance/persistence of infection (Welburn and Maudlin, 2012; Camara et al., 2021). Vector control therefore appears as a viable alternative to accelerate sleeping sickness transmission interruption, and WHO has identified some critical actions for HAT elimination, including the coordination of vector control and animal trypanosomiasis management among countries, stakeholders and other sectors (e.g. tourism and wildlife) through multisectoral national bodies to maximize synergies (WHO, 2021). The paper by Kagbadouno and Collaborators (2024) uses microsatellite markers genotyping and population genetics tools to investigate the impact of 11 years of tiny target-based vector control on the population biology of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in Boffa, one of the three active sleeping sickness foci in Guinea (Kagbadouno et al., 2012). Although vector control significantly reduced the apparent densities of tsetse flies (and therefore the human exposure to the vector) as well as the prevalence and incidence of the disease in the Boffa HAT focus (Courtin et al., 2015), no genetic signature of vector control was observed as no difference in population size, before and after the onset of the control policy, was found. The authors then provided national programs and implementing partners with indications on the actions to be taken to (i) maintain the achievements of vector control (thus avoiding rebound/resurgence as was experienced in the past (Franco et al., 2014), and (ii) accelerate the momentum towards elimination by for example combining these vector control efforts with medical surveys for case detection and treatment, in line with WHO recommendations (WHO, 2021). References Camara M, Soumah AM, Ilboudo H, Travaillé C, Clucas C, Cooper A, Kuispond Swar NR, Camara O, Sadissou I, Calvo Alvarez E, Crouzols A, Bart JM, Jamonneau V, Camara M, MacLeod A, Bucheton B, Rotureau B. Extravascular Dermal Trypanosomes in Suspected and Confirmed Cases of gambiense Human African Trypanosomiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 1;73(1):12-20. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa897 Courtin F, Camara M, Rayaisse JB, Kagbadouno M, Dama E, Camara O, Traore IS, Rouamba J, Peylhard M, Somda MB, Leno M, Lehane MJ, Torr SJ, Solano P, Jamonneau V, Bucheton B (2015) Reducing human-tsetse contact significantly enhances the efficacy of sleeping sickness active screening campaigns: a promising result in the context of elimination. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003727 Franco JR, Simarro PP, Diarra A, Jannin JG. (2014) Epidemiology of human African trypanosomiasis. Clin Epidemiol. 6:257-75. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S39728 Kagbadouno, M. S., Séré, M., Ségard, A., Camara, A. D., Camara, M., Bucheton, B., ... & Ravel, S. (2023). Population genetics of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the disease. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.25.550445 Kagbadouno MS, Camara M, Rouamba J, Rayaisse JB, Traoré IS, Camara O, Onikoyamou MF, Courtin F, Ravel S, De Meeûs T, Bucheton B, Jamonneau V, Solano P (2012) Epidemiology of sleeping sickness in boffa (Guinea): where are the trypanosomes? PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 6, e1949. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001949 Moore A, Richer M, Enrile M, Losio E, Roberts J, Levy D. Resurgence of sleeping sickness in Tambura County, Sudan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999 Aug;61(2):315-8. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1999.61.315 Sah R, Mohanty A, Rohilla R, Padhi BK. A resurgence of Sleeping sickness amidst the COVID-19 pandemic: Correspondence. Int J Surg Open. 2023 Apr;53:100604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijso.2023.100604 Welburn SC, Maudlin I. Priorities for the elimination of sleeping sickness. Adv Parasitol. 2012;79:299-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398457-9.00004-4 World Health Organization, 2021. Ending the neglect to attain the Sustainable Development Goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. ISBN: 978 92 4 001035 2. 196p. World Health Organization, 2023a. Trypanosomiasis, human African (sleeping sickness): key facts. Accessed at https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trypanosomiasis-human-african-(sleeping-sickness) on February 19, 2023. World Health Organization, 2023b. Human African Trypanosomiasis, (sleeping sickness): the global health observatory. Accessed at https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/human-african-trypanosomiasis on February 19, 2023. | Population genetics of *Glossina palpalis* gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the disease | Moise S. Kagbadouno, Modou Séré, Adeline Ségard, Abdoulaye Dansy Camara, Mamadou Camara, Bruno Bucheton, Jean-Mathieu Bart, Fabrice Courtin, Thierry de Meeûs, Sophie Ravel | <p style="text-align: justify;">Human African trypanosomosis (HAT), also known as sleeping sickness, is still a major concern in endemic countries. Its cyclical vector are biting insects of the genus Glossina or tsetse flies. In Guinea, the mangro... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors | Hugues Nana Djeunga | 2023-07-29 13:24:52 | View | ||
08 Aug 2023
A global Corynebacterium diphtheriae genomic framework sheds light on current diphtheria reemergenceMelanie Hennart, Chiara Crestani, Sebastien Bridel, Nathalie Armatys, Sylvie Brémont, Annick Carmi-Leroy, Annie Landier, Virginie Passet, Laure Fonteneau, Sophie Vaux, Julie Toubiana, Edgar Badell, Sylvain Brisse https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.20.529124DIPHTOSCAN : A new tool for the genomic surveillance of diphtheriaRecommended by Rodolfo García-Contreras based on reviews by Ankur Mutreja and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the greatest achievements of health sciences is the eradication of infectious diseases such as smallpox that in the past imposed a severe burden on humankind, through global vaccination campaigns. Moreover, progress towards the eradication of others such as poliomyelitis, dracunculiasis, and yaws is being made. In contrast, other infections that were previously contained are reemerging, due to several factors, including lack of access to vaccines due to geopolitical reasons, the rise of anti-vaccine movements, and the constant mobility of infected persons from the endemic sites. One of such disease is diphtheria, caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae and a few other related species such as C. ulcerans and C. pseudotuberculosis. Importantly, in France, diphtheria cases reported in 2022 increased 7-fold from the average of previously recorded cases per year in the previous 4 years and the situation in other European countries is similar. Hence, as reported here, Hennart et al. (2023) developed DIPHTOSCAN, a free access bioinformatics tool with user-friendly interphase, aimed to easily identify, extract and interpret important genomic features such as the sublineage of the strain, the presence of the tox gene (as a string predictor for toxigenic disease) as well as genes coding other virulence factors such as fimbriae, and the presence of know resistant mechanisms towards antibiotics like penicillin and erythromycin currently used in the clinic to treat this infection. The authors validated the performance of their tool with a large collection of genomes, including those obtained from the isolates of the 2022 outbreak in France, more than 1,200 other genomes isolated from France, Algeria, and Yemen, and more than 500 genomes from several countries from Europe, America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania that are available through the NCBI site. DIPHTOSCAN will allow the rapid identification and surveillance of potentially dangerous strains such as those being tox-positive isolates and resistant to multiple drugs and/or first-line treatments and a better understanding of the epidemiology and evolution of this important reemerging disease. | A global *Corynebacterium diphtheriae* genomic framework sheds light on current diphtheria reemergence | Melanie Hennart, Chiara Crestani, Sebastien Bridel, Nathalie Armatys, Sylvie Brémont, Annick Carmi-Leroy, Annie Landier, Virginie Passet, Laure Fonteneau, Sophie Vaux, Julie Toubiana, Edgar Badell, Sylvain Brisse | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background</strong></p> <p style="text-align: justify;">Diphtheria, caused by <em>Corynebacterium diphtheriae</em>, reemerges in Europe since 2022. Genomic sequencing can inform on transmission routes and g... | Drug resistance, tolerance and persistence, Epidemiology, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Microbiology of infections, Population genetics of hosts, infectiou... | Rodolfo García-Contreras | Ankur Mutreja | 2023-03-09 16:02:27 | View | |
27 Feb 2023
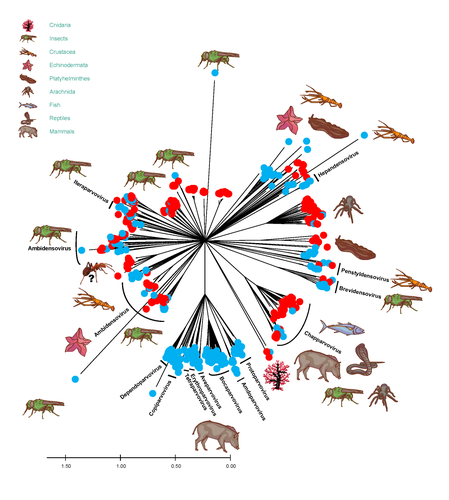
African army ants at the forefront of virome surveillance in a remote tropical forestMatthieu Fritz, Berenice Reggiardo, Denis Filloux, Lisa Claude, Emmanuel Fernandez, Frederic Mahe, Simona Kraberger, Joy M. Custer, Pierre Becquart, Telstar Ndong Mebaley, Linda Bohou Kombila, Leadisaelle H. Lenguiya, Larson Boundenga, Illich M. Mombo, Gael Darren Maganga, Fabien R. Niama, Jean-Sylvain Koumba, Mylene Ogliastro, Michel Yvon, Darren Martin, Stephane Blanc, Arvind Varsani, Eric Leroy, Philippe Roumagnac https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.13.520061A groundbreaking study using ants revealed a spectacular diversity of viruses in hardly accessible ecosystems like tropical forestsRecommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Mart Krupovic and 1 anonymous reviewerDeciphering the virome (the set or assemblage of viruses) of the Earth, from individual organisms to entire ecosystems, has become a key priority. The first step to better understanding the impact of viruses on the ecology and functions of ecosystems is to describe their diversity. Such knowledge opens the gates to a better assessment of global nutrient cycling or of the threat that viruses represent to individual health. This explains the increasing number of pioneering studies that are currently sequencing the complete or partial genome of thousands of new viruses [1]. In their exciting study, Fritz and collaborators [2], authors sampled 209 army ants (Genus Dorylus) to investigate the virus diversity in dense forests that researchers cannot easily access. Indeed, these ants live in colonies (21 were sampled) that can move 1 km per day, covering a significant area and attacking many invertebrate and vertebrate preys. Each sample was sequenced by a protocol called VANA sequencing and allowing the enrichment of the sample in viral sequences [3], so improving the detection of viruses present at low abundance in the ant (and more specifically in its gut for viruses infecting preys). Around 45,000 contigs presented homologies with bacterial, plant, invertebrate, and vertebrate infecting viruses. Half could be assigned to 56 families and 157 genera of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Beyond this amazing harvest of new and known virus sequences using an original methodology, the results significantly improve the current frontiers of known viral taxonomy and diversity and raise exciting research tracks to expand them. As a preprint, several blogs or news of leading scientists and journals have already highlighted this study. For example, in the news section of Science magazine, Jon Cohen underlined the originality of the approach for virus hunting on Earth with the title “Armed with air samplers, rope tricks, and—yes—ants, virus hunters spot threats in new ways”[4]. Another example is the mention of the publication by Elisabeth Bik in her Microbiome Digest: she wrote, “An amazing read is a fresh preprint from Fritz and collaborator describing an exciting method of sampling in difficult-to-reach environments“ [5]. The paper from Fritz et al [2] thus represents a significant advance in virus ecology, as already recognized by early readers, and this is why I strongly recommend its publication in PCI Infections. REFERENCES 1. Edgar RC, Taylor J, Lin V, Altman T, Barbera P, Meleshko D, Lohr D, Novakovsky G, Buchfink B, Al-Shayeb B, Banfield JF, de la Peña M, Korobeynikov A, Chikhi R, Babaian A (2022) Petabase-scale sequence alignment catalyses viral discovery. Nature, 602, 142–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04332-2 2. Fritz M, Reggiardo B, Filloux D, Claude L, Fernandez E, Mahé F, Kraberger S, Custer JM, Becquart P, Mebaley TN, Kombila LB, Lenguiya LH, Boundenga L, Mombo IM, Maganga GD, Niama FR, Koumba J-S, Ogliastro M, Yvon M, Martin DP, Blanc S, Varsani A, Leroy E, Roumagnac P (2023) African army ants at the forefront of virome surveillance in a remote tropical forest. bioRxiv, 2022.12.13.520061, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.13.520061 3. François S, Filloux D, Fernandez E, Ogliastro M, Roumagnac P (2018) Viral Metagenomics Approaches for High-Resolution Screening of Multiplexed Arthropod and Plant Viral Communities. In: Viral Metagenomics: Methods and Protocols Methods in Molecular Biology. (eds Pantaleo V, Chiumenti M), pp. 77–95. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7683-6_7 4. Cohen J (2023) Virus hunters test new surveillance tools. Science, 379, 16–17. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg5292 5. Ponsero A (2023) February 18th, 2023. Microbiome Digest - Bik’s Picks. https://microbiomedigest.com/2023/02/18/february-18th-2023/ | African army ants at the forefront of virome surveillance in a remote tropical forest | Matthieu Fritz, Berenice Reggiardo, Denis Filloux, Lisa Claude, Emmanuel Fernandez, Frederic Mahe, Simona Kraberger, Joy M. Custer, Pierre Becquart, Telstar Ndong Mebaley, Linda Bohou Kombila, Leadisaelle H. Lenguiya, Larson Boundenga, Illich M. M... | <p style="text-align: justify;">In this study, we used a predator-enabled metagenomics strategy to sample the virome of a remote and difficult-to-access densely forested African tropical region. Specifically, we focused our study on the use of arm... |  | Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, One Health, Reservoirs, Viruses | Sebastien Massart | 2022-12-14 11:57:40 | View | |
19 Jul 2023
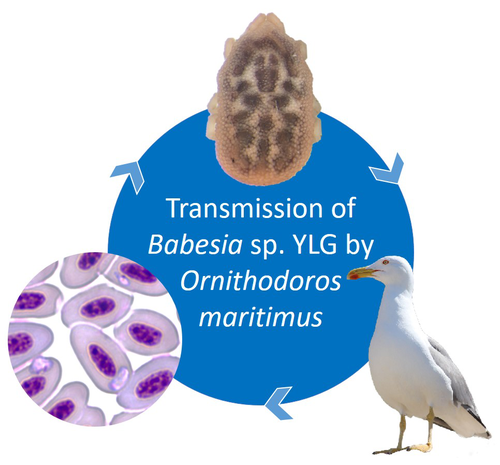
A soft tick vector of Babesia sp. YLG in Yellow-legged gull (Larus michahellis) nestsClaire Bonsergent, Marion Vittecoq, Carole Leray, Maggy Jouglin, Marie Buysse, Karen D. McCoy, Laurence Malandrin https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.24.534071A four-year study reveals the potential role of the soft tick Ornithodoros maritimus in the transmission and circulation of Babesia sp. YLG in Yellow-legged gull colonies.Recommended by Thomas Pollet based on reviews by Hélène Jourdan-Pineau and Tahar KernifWorldwide, ticks and tick-borne diseases are a persistent example of problems at the One Health interface between humans, wildlife, and environment (1, 2). The management and prevention of ticks and tick-borne diseases require a better understanding of host, tick and pathogen interactions and thus get a better view of the tick-borne pathosystems. In this study (3), the tick-borne pathosystem included three component species: first a seabird host, the Yellow-legged gull (YLG - Larus michahellis, Laridae), second a soft nidicolous tick (Ornithodoros maritimus, Argasidae, syn. Alectorobius maritimus) known to infest this host and third a blood parasite (Babesia sp. YLG, Piroplasmidae). In this pathosystem, authors investigated the role of the soft tick, Ornithodoros maritimus, as a potential vector of Babesia sp. YLG. They analyzed the transmission of Babesia sp. YLG by collecting different tick life stages from YLG nests during 4 consecutive years on the islet of Carteau (Gulf of Fos, Camargue, France). Ticks were dissected and organs were analyzed separately to detect the presence of Babesia sp DNA and to evaluate different transmission pathways. While the authors detected Babesia sp. YLG DNA in the salivary glands of nymphs, females and males, this result reveals a strong suspicion of transmission of the parasite by the soft tick. Babesia sp. YLG DNA was also found in tick ovaries, which could indicate possible transovarial transmission. Finally, the authors detected Babesia sp. YLG DNA in several male testes and in endospermatophores, and notably in a parasite-free female (uninfected ovaries and salivary glands). These last results raise the interesting possibility of sexual transmission from infected males to uninfected females. As pointed out by both reviewers, this is a nice study, well written and easy to read. All the results are new and allow to better understand the role of the soft tick, Ornithodoros maritimus, as a potential vector of Babesia sp. YLG. They finally question about the degree to which the parasite can be maintained locally by ticks and the epidemiological consequences of infection for both O. maritimus and its avian host. For all these reasons, I chose to recommend this article for Peer Community In Infections. References
| A soft tick vector of *Babesia* sp. YLG in Yellow-legged gull (*Larus michahellis*) nests | Claire Bonsergent, Marion Vittecoq, Carole Leray, Maggy Jouglin, Marie Buysse, Karen D. McCoy, Laurence Malandrin | <p style="text-align: justify;"><em>Babesia </em>sp. YLG has recently been described in Yellow-legged gull (<em>Larus michahellis</em>) chicks and belongs to the Peircei clade in the new classification of Piroplasms. Here, we studied <em>Babesia <... |  | Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Eukaryotic pathogens/symbionts, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Parasites, Vectors | Thomas Pollet | 2023-03-29 14:33:40 | View | |
24 Jun 2024
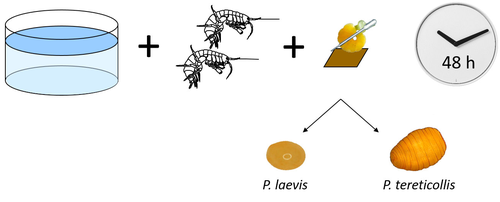
Differences in specificity, development time and virulence between two acanthocephalan parasites, infecting two cryptic species of Gammarus fossarumAlexandre Bauer, Lucie Develay Nguyen, Sébastien Motreuil, Maria Teixeira, Nelly Debrosse, Thierry Rigaud https://hal.science/hal-04455823Gammarid is not equal gammarid for acanthocephalan parasitesRecommended by Daniel Grabner based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe question on the role of different alternative hosts in the life cycle of acanthocephalan parasites has not been fully resolved to date. There is some information on the use of fish hosts in the genus Pomphorhynchus (Perrot-Minnot et al. 2019). It is known that acanthocephalans of the genus Pomphorhynchus can infect a number of different amphipod species (e.g. Bauer et al. 2000; Cornet et al. 2010; Dezfuli et al. 1999) but it is not clear if some host species might be more “advantageous” for the parasite, or if the parasite is more virulent to some host species than to others. Bauer et al. (2024) investigated different well characterized cryptic lineages of Gammarus fossarum (Weiss et al. 2013) for their susceptibility for two Pomphorhynchus sp. The results show that there is a difference in susceptibility to acanthocephalans between different linages of G. fossarum. Additionally, a parasite species specific difference was detected: the difference in susceptibility was more pronounced for P. tereticollis than for P. laevis. P. tereticollis was less virulent and developed slower than P. laevis (in G. fossarum). Besides the improved understanding of the biology of acanthocephalan parasites, this study clearly points out that we have to be careful with putting the “generalist” label on parasites simply due to the number of alternative host species we find them in. Instead, we should always have in mind that some of these hosts might be less suitable for the parasite than others when comparing quantitative data on the infection success. I highly appreciate the experimental approach taken that allows more profound conclusions than evaluations of field data. Experiments and analyses have been conducted well. I think this paper is significantly enhancing our knowledge on the specificity for the intermediate host. I find it highly remarkable that this was even found among different host lineages. References Bauer, A., Trouve, S., Gregoire, A., Bollache, L., Cezilly, F. (2000) Differential influence of Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) on the behaviour of native and invader gammarid species. International Journal for Parasitology, 30(14), 1453-1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(00)00138-7 Bauer, A., Develay Nguyen, L., Motreuil, S., Teixeira, M., Debrosse, N., Rigaud, T. (2024) Experimental infections reveal differences in specificity, development time and virulence between the acanthocephalan parasite Pomphorhynchus tereticollis and its sympatric counterpart P. laevis, in two cryptic species of Gammarus fossarum. HAL, Ver. 2, Peer-Reviewed and Recommended by Peer Community in Infections, hal-04455823. https://hal.science/hal-04455823 Cornet, S., Sorci, G., Moret, Y. (2010) Biological invasion and parasitism: invaders do not suffer from physiological alterations of the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis. Parasitology, 137(1), 137-147. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182009991077 Dezfuli, B.S., Rossetti, E., Bellettato, C.M., Maynard, B.J. (1999) Pomphorhynchus laevis in its intermediate host Echinogammarus stammeri in the River Brenta, Italy. Journal of Helminthology, 73(2), 95-102. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X00700277 Perrot-Minnot, M.J., Guyonnet, E., Bollache, L., Lagrue, C. (2019) Differential patterns of definitive host use by two fish acanthocephalans occurring in sympatry: Pomphorhynchus laevis and Pomphorhynchus tereticollis. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 8, 135-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.01.007 Weiss, M., Macher, J.N., Seefeldt, M.A., Leese, F. (2013) Molecular evidence for further overlooked species within the Gammarus fossarum complex (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Hydrobiologia, 721(1), 165-184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1658-7
| Differences in specificity, development time and virulence between two acanthocephalan parasites, infecting two cryptic species of *Gammarus fossarum* | Alexandre Bauer, Lucie Develay Nguyen, Sébastien Motreuil, Maria Teixeira, Nelly Debrosse, Thierry Rigaud | <p style="text-align: justify;">Multi-host parasites can exploit various host species that differ in abundance and susceptibility to infection, which will contribute unequally to their transmission and fitness. Several species of acanthocephalan m... |  | Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Resistance/Virulen... | Daniel Grabner | 2024-02-14 13:39:19 | View | |
02 Jun 2023
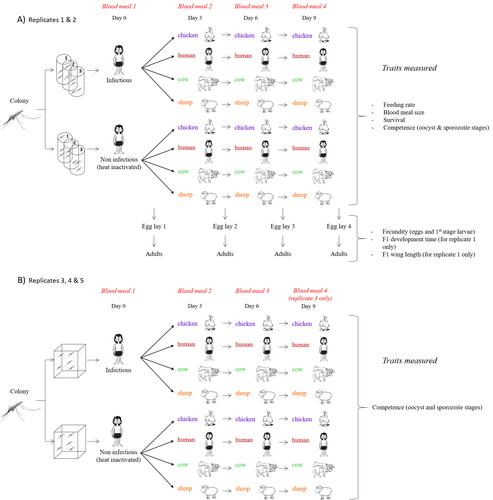
Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmissionAmélie Vantaux, Nicolas Moiroux, Kounbobr Roch Dabiré, Anna Cohuet, Thierry Lefèvre https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.10.527988What you eat can eliminate you: bloodmeal sources and mosquito fitnessRecommended by Diego Santiago-Alarcon based on reviews by Francisco C. Ferreira and 1 anonymous reviewerDiptera-borne pathogens rank among the most serious health threats to vertebrate organisms around the world, particularly in tropical areas undergoing strong human impacts – e.g., urbanization and farming –, where social unrest and poor economies exacerbate the risk (Allen et al. 2017; Robles-Fernández et al. 2022). Although scientists have acquired a detailed knowledge on the life-history of malaria parasites (Pacheco and Escalante 2023), they still do not have enough information about their insect vectors to make informed management and preventive decisions (Santiago-Alarcon 2022). In this sense, I am pleased to recommend the study of Vantaux et al. (2023), where authors conducted an experimental and theoretical study to analyzed how the diversity of blood sources (i.e., human, cattle, sheep, and chicken) affected the fitness of the human malaria parasite – Plasmodium falciparum – and its mosquito vector – Anopheles gambiae s.l. The study was conducted in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Interestingly, authors did not find a significant effect of blood meal source on parasite development, and a seemingly low impact on the fitness of mosquitoes that were exposed to parasites. However, mosquitoes’ feeding rate, survival, fecundity, and offspring size were negatively affected by the type of blood meal ingested. In general, chicken blood represented the worst meal source for the different measures of mosquito fitness, and sheep blood seems to be the least harmful. This result was supported by the theoretical model, where vectorial capacity was always better when mosquitoes fed on sheep blood compared to cow and chicken blood. Thus, the knowledge generated by this study provides a pathway to reduce human infection risk by managing the diversity of farm animals. For instance, transmission to humans can decrease when chickens and cows represent most of the available blood sources in a village. These results along with other interesting details of this study, represent a clear example of the knowledge and understanding of insect vectors that we need to produce in the future, particularly to manage and prevent hazards and risks (sensu Hoseini et al. 2017). REFERENCES Allen T., et al., Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 8, 1124. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00923-8 Hosseini P.R., et al., Does the impact of biodiversity differ between emerging and endemic pathogens? The need to separate the concepts of hazard and risk. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 372, 20160129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0129 Pacheco M.A., and Escalante, A.A., Origin and diversity of malaria parasites and other Haemosporida. Trend. Parasitol. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2023.04.004 Robles-Fernández A., et al., Wildlife susceptibility to infectious diseases at global scales. PNAS 119: e2122851119. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2122851119 Santiago-Alarcon D. A meta-analytic approach to investigate mosquitoes’ (Diptera: Culicidae) blood feeding preferences from non-urban to urban environments. In: Ecology and Control of Vector-borne Diseases, vol. 7 (R.G. Gutiérrez-López, J.G. Logan, Martínez-de la Puente J., Eds). Pp. 161-177. Wageningen Academic Publishers. eISBN: 978-90-8686-931-2 | ISBN: 978-90-8686-379-2 (2022). Vantaux A. et al. Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections (2023). https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.10.527988 | Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission | Amélie Vantaux, Nicolas Moiroux, Kounbobr Roch Dabiré, Anna Cohuet, Thierry Lefèvre | <p style="text-align: justify;">The transmission of malaria parasites from mosquito to human is largely determined by the dietary specialization of <em>Anopheles mosquitoes</em> to feed on humans. Few studies have explored the impact of blood meal... |  | Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Vectors | Diego Santiago-Alarcon | 2023-02-13 11:02:58 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Jorge Amich
Christine Chevillon
Fabrice Courtin
Christine Coustau
Thierry De Meeûs
Heather R. Jordan
Karl-Heinz Kogel
Yannick Moret
Thomas Pollet
Benjamin Roche
Benjamin Rosenthal
Bashir Salim
Lucy Weinert










