
MASSART Sebastien
- Laboratory of Plant pathology - TERRA - Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech, Liege University, Liege, Belgium
- Epidemiology, Pathogenic/Symbiotic Fungi, Phytopathology, Plant diseases, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Viruses
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
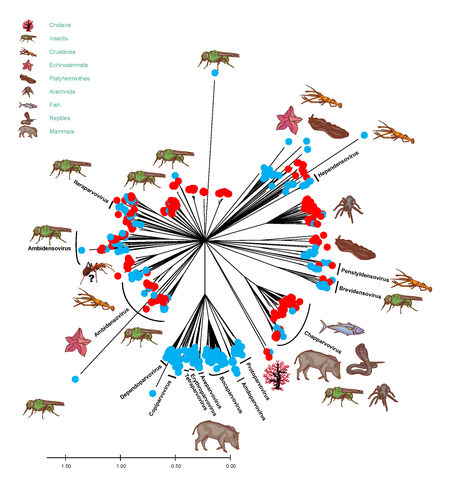
African army ants at the forefront of virome surveillance in a remote tropical forest
A groundbreaking study using ants revealed a spectacular diversity of viruses in hardly accessible ecosystems like tropical forests
Recommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Mart Krupovic and 1 anonymous reviewerDeciphering the virome (the set or assemblage of viruses) of the Earth, from individual organisms to entire ecosystems, has become a key priority. The first step to better understanding the impact of viruses on the ecology and functions of ecosystems is to describe their diversity. Such knowledge opens the gates to a better assessment of global nutrient cycling or of the threat that viruses represent to individual health. This explains the increasing number of pioneering studies that are currently sequencing the complete or partial genome of thousands of new viruses [1].
In their exciting study, Fritz and collaborators [2], authors sampled 209 army ants (Genus Dorylus) to investigate the virus diversity in dense forests that researchers cannot easily access. Indeed, these ants live in colonies (21 were sampled) that can move 1 km per day, covering a significant area and attacking many invertebrate and vertebrate preys. Each sample was sequenced by a protocol called VANA sequencing and allowing the enrichment of the sample in viral sequences [3], so improving the detection of viruses present at low abundance in the ant (and more specifically in its gut for viruses infecting preys).
Around 45,000 contigs presented homologies with bacterial, plant, invertebrate, and vertebrate infecting viruses. Half could be assigned to 56 families and 157 genera of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Beyond this amazing harvest of new and known virus sequences using an original methodology, the results significantly improve the current frontiers of known viral taxonomy and diversity and raise exciting research tracks to expand them.
As a preprint, several blogs or news of leading scientists and journals have already highlighted this study. For example, in the news section of Science magazine, Jon Cohen underlined the originality of the approach for virus hunting on Earth with the title “Armed with air samplers, rope tricks, and—yes—ants, virus hunters spot threats in new ways”[4]. Another example is the mention of the publication by Elisabeth Bik in her Microbiome Digest: she wrote, “An amazing read is a fresh preprint from Fritz and collaborator describing an exciting method of sampling in difficult-to-reach environments“ [5].
The paper from Fritz et al [2] thus represents a significant advance in virus ecology, as already recognized by early readers, and this is why I strongly recommend its publication in PCI Infections.
REFERENCES
1. Edgar RC, Taylor J, Lin V, Altman T, Barbera P, Meleshko D, Lohr D, Novakovsky G, Buchfink B, Al-Shayeb B, Banfield JF, de la Peña M, Korobeynikov A, Chikhi R, Babaian A (2022) Petabase-scale sequence alignment catalyses viral discovery. Nature, 602, 142–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04332-2
2. Fritz M, Reggiardo B, Filloux D, Claude L, Fernandez E, Mahé F, Kraberger S, Custer JM, Becquart P, Mebaley TN, Kombila LB, Lenguiya LH, Boundenga L, Mombo IM, Maganga GD, Niama FR, Koumba J-S, Ogliastro M, Yvon M, Martin DP, Blanc S, Varsani A, Leroy E, Roumagnac P (2023) African army ants at the forefront of virome surveillance in a remote tropical forest. bioRxiv, 2022.12.13.520061, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.13.520061
3. François S, Filloux D, Fernandez E, Ogliastro M, Roumagnac P (2018) Viral Metagenomics Approaches for High-Resolution Screening of Multiplexed Arthropod and Plant Viral Communities. In: Viral Metagenomics: Methods and Protocols Methods in Molecular Biology. (eds Pantaleo V, Chiumenti M), pp. 77–95. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-7683-6_7
4. Cohen J (2023) Virus hunters test new surveillance tools. Science, 379, 16–17. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adg5292
5. Ponsero A (2023) February 18th, 2023. Microbiome Digest - Bik’s Picks. https://microbiomedigest.com/2023/02/18/february-18th-2023/

Transcriptome responses of the aphid vector Myzus persicae are shaped by identities of the host plant and the virus
How do multiple host plants and virus species challenge aphid molecular machinery?
Recommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Juan José Lopez Moya and Michelle HeckThe impact of virus infection of a plant on an aphid’s behaviour has been observed in many studies [1]. Indeed, virus infection can alter plant biochemistry through the emission of volatile organic compounds and plant tissue content modification. These alterations can further impact the interactions between plants and aphids. However, although it is a well-known phenomenon, very few studies have explored the consequences of plant virus infection on the gene expression of aphids to understand better the aphid’s manipulation by the plant virus. In this context, the recommended study [2] reports a comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of the genes expressed by one aphid species, Myzus persicae, a vector of several plant viruses, when feeding on plants. Michelle Heck underlined how significant this study is for comprehending the molecular bases of aphid-vector manipulation by plant viruses (see below).
Interestingly, the study design has integrated several factors that might influence the gene expression of M. persicae when feeding on the plant. Indeed, the authors investigated the effect of two plant species (Arabidopsis thaliana and Camelia sativa) and two virus species [turnip yellows virus (TuYV) and cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV)]. Noteworthy, the transmission mode of TuYV is circulative and persistent, while CaMV is transmitted by a semi-persistent non-circulative mode. As Juan José Lopez Moya mentioned, multiple comparisons allowed the identification of the different responses of aphids in front of different host plants infected or not by different viruses (see below). This publication is complementary to a previous publication from the same team focusing on plant transcriptome analysis [3].
Thanks to their experimental design, the authors identified genes commonly deregulated by both viruses and/or both plant species and deregulated genes by a single virus or a single plant. Figure 4 nicely summarizes the number of deregulated genes. A thorough discussion on the putative role of deregulated genes in different conditions gave a comprehensive follow-up of the results and their impact on the current knowledge of plant-virus-vector interactions.
This study has now opened the gate to promising research focusing on the functional validation of the identified genes while also narrowing the study from the body to the tissue level.
References:
1. Carr JP, Tungadi T, Donnelly R, Bravo-Cazar A, Rhee S-J, Watt LG, Mutuku JM, Wamonje FO, Murphy AM, Arinaitwe W, Pate AE, Cunniffe NJ, Gilligan CA (2020) Modelling and manipulation of aphid-mediated spread of non-persistently transmitted viruses. Virus Research, 277, 197845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2019.197845
2. Chesnais Q, Golyaev V, Velt A, Rustenholz C, Verdier M, Brault V, Pooggin MM, Drucker M (2022) Transcriptome responses of the aphid vector Myzus persicae are shaped by identities of the host plant and the virus. bioRxiv , 2022.07.18.500449, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500449
3. Chesnais Q, Golyaev V, Velt A, Rustenholz C, Brault V, Pooggin MM, Drucker M (2022) Comparative Plant Transcriptome Profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 and Camelina sativa var. Celine Infested with Myzus persicae Aphids Acquiring Circulative and Noncirculative Viruses Reveals Virus- and Plant-Specific Alterations Relevant to Aphid Feeding Behavior and Transmission. Microbiology Spectrum, 10, e00136-22. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.00136-22