
SANTIAGO-ALARCON Diego
- Integrative Biology, University of South Florida, Tampa, United States of America
- Animal diseases, Coevolution, Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Geography of infectious diseases, Infections and conservation biology (of plants, or animals), Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Phylogenetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Population dynamics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Vectors
- recommender
Recommendation: 1
Reviews: 0
Recommendation: 1
Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission
What you eat can eliminate you: bloodmeal sources and mosquito fitness
Recommended by Diego Santiago-Alarcon based on reviews by Francisco C. Ferreira and 1 anonymous reviewerDiptera-borne pathogens rank among the most serious health threats to vertebrate organisms around the world, particularly in tropical areas undergoing strong human impacts – e.g., urbanization and farming –, where social unrest and poor economies exacerbate the risk (Allen et al. 2017; Robles-Fernández et al. 2022). Although scientists have acquired a detailed knowledge on the life-history of malaria parasites (Pacheco and Escalante 2023), they still do not have enough information about their insect vectors to make informed management and preventive decisions (Santiago-Alarcon 2022).
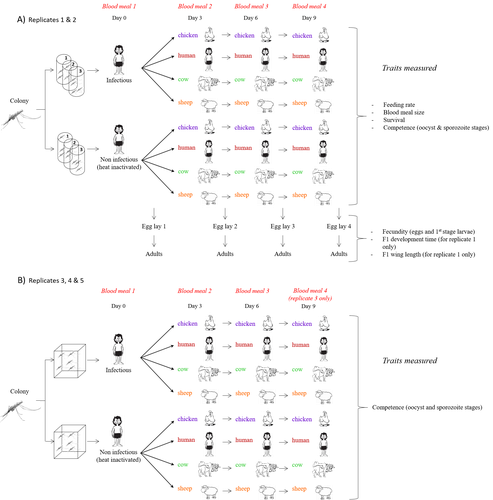
In this sense, I am pleased to recommend the study of Vantaux et al. (2023), where authors conducted an experimental and theoretical study to analyzed how the diversity of blood sources (i.e., human, cattle, sheep, and chicken) affected the fitness of the human malaria parasite – Plasmodium falciparum – and its mosquito vector – Anopheles gambiae s.l.
The study was conducted in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Interestingly, authors did not find a significant effect of blood meal source on parasite development, and a seemingly low impact on the fitness of mosquitoes that were exposed to parasites. However, mosquitoes’ feeding rate, survival, fecundity, and offspring size were negatively affected by the type of blood meal ingested. In general, chicken blood represented the worst meal source for the different measures of mosquito fitness, and sheep blood seems to be the least harmful. This result was supported by the theoretical model, where vectorial capacity was always better when mosquitoes fed on sheep blood compared to cow and chicken blood. Thus, the knowledge generated by this study provides a pathway to reduce human infection risk by managing the diversity of farm animals. For instance, transmission to humans can decrease when chickens and cows represent most of the available blood sources in a village.
These results along with other interesting details of this study, represent a clear example of the knowledge and understanding of insect vectors that we need to produce in the future, particularly to manage and prevent hazards and risks (sensu Hoseini et al. 2017).
REFERENCES
Allen T., et al., Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 8, 1124. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00923-8
Hosseini P.R., et al., Does the impact of biodiversity differ between emerging and endemic pathogens? The need to separate the concepts of hazard and risk. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 372, 20160129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0129
Pacheco M.A., and Escalante, A.A., Origin and diversity of malaria parasites and other Haemosporida. Trend. Parasitol. (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2023.04.004
Robles-Fernández A., et al., Wildlife susceptibility to infectious diseases at global scales. PNAS 119: e2122851119. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2122851119
Santiago-Alarcon D. A meta-analytic approach to investigate mosquitoes’ (Diptera: Culicidae) blood feeding preferences from non-urban to urban environments. In: Ecology and Control of Vector-borne Diseases, vol. 7 (R.G. Gutiérrez-López, J.G. Logan, Martínez-de la Puente J., Eds). Pp. 161-177. Wageningen Academic Publishers. eISBN: 978-90-8686-931-2 | ISBN: 978-90-8686-379-2 (2022).
Vantaux A. et al. Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections (2023). https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.10.527988