Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers▼ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
14 Nov 2022
Ehrlichia ruminantium uses its transmembrane protein Ape to adhere to host bovine aortic endothelial cellsValérie Pinarello, Elena Bencurova, Isabel Marcelino, Olivier Gros, Carinne Puech, Mangesh Bhide, Nathalie Vachiery, Damien F. Meyer https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.15.447525Adhesion process of Ehrlichia ruminantium to its host cell: the role of the protein ERGACDS01230 elucidatedRecommended by Thomas Pollet based on reviews by Rodolfo García-Contreras and Alejandro Cabezas-CruzAs recently reported by the world organisation for animal health, 60% of infectious diseases are zoonotic with a significant part associated to ticks. Ticks can transmit various pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and parasites. Among pathogens known to be transmitted by ticks, Ehrlichia ruminantium is an obligate intracellular Gram-negative bacterium responsible for the fatal heartwater disease of domestic and wild ruminants (Allsopp, 2010). E. ruminantium is transmitted by ticks of the genus Amblyomma in the tropical and sub-Saharan areas, as well as in the Caribbean islands. It constitutes a major threat for the American livestock industries since a suitable tick vector is already present in the American mainland and potential introduction of infected A. variegatum through migratory birds or uncontrolled movement of animals from Caribbean could occur (i.e. Deem, 1998 ; Kasari et al 2010). The disease is also a major obstacle to the introduction of animals from heartwater-free to heartwater-infected areas into sub-Saharan Africa and thus restrains breeding programs aiming at upgrading local stocks (Allsopp, 2010). In this context, it is essential to develop control strategies against heartwater, as developing effective vaccines, for instance. Such an objective requires a better understanding of the early interaction of E. ruminantium and its host cells and of the mechanisms associated with bacterial adhesion to the host-cell. In this study, the authors. studied the role of E. ruminantium membrane protein ERGA_CDS_01230 in the adhesion process to host bovine aortic endothelial cells (BAEC). After successfully producing the recombinant version of the protein, Pinarello et al (2022) followed the in vitro culture of E. ruminantium in BAEC and observed that the expression of the protein peaked at the extracellular infectious elementary body stages. This result would suggest the likely involvement of the protein in the early interaction of E. ruminantium with its host cells. The authors then showed using flow cytometry, and scanning electron microscopy, that beads coated with the recombinant protein adhered to BAEC. In addition, they also observed that the adhesion protein of E. ruminantium interacted with proteins of the cell's lysate, membrane and organelle fractions. Additionally, enzymatic treatment, degrading dermatan and chondroitin sulfates on the surface of BAEC, was associated with a 50% reduction in the number of bacteria in the host cell after a development cycle, indicating that glycosaminoglycans might play a role in the adhesion of E. ruminantium to the host-cell. Finally, the authors observed that the adhesion protein of E. ruminantium induced a humoral response in vaccinated animals, making this protein a possible vaccine candidate. As rightly pointed out by both reviewers, the results of this study represent a significant advance (i) in the understanding of the role of the E. ruminantium membrane protein ERGA_CDS_01230 in the adhesion process to the host-cell and (ii) in the development of new control strategies against heartwater as this protein might potentially be used as an immunogen for the development of future vaccines. References Allsopp, B.A. (2010). Natural history of Ehrlichia ruminantium. Vet Parasitol 167, 123-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2009.09.014 Deem, S.L. (1998). A review of heartwater and the threat of introduction of Cowdria ruminantium and Amblyomma spp. ticks to the American mainland. J Zoo Wildl Med 29, 109-113. Kasari, T.R. et al (2010). Recognition of the threat of Ehrlichia ruminantium infection in domestic and wild ruminants in the continental United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 237:520-30. https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.237.5.520 Pinarello V, Bencurova E, Marcelino I, Gros O, Puech C, Bhide M, Vachiery N, Meyer DF (2022) Ehrlichia ruminantium uses its transmembrane protein Ape to adhere to host bovine aortic endothelial cells. bioRxiv, 2021.06.15.447525, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.15.447525 | *Ehrlichia ruminantium* uses its transmembrane protein Ape to adhere to host bovine aortic endothelial cells | Valérie Pinarello, Elena Bencurova, Isabel Marcelino, Olivier Gros, Carinne Puech, Mangesh Bhide, Nathalie Vachiery, Damien F. Meyer | <p><em>Ehrlichia ruminantium</em> is an obligate intracellular bacterium, transmitted by ticks of the genus <em>Amblyomma</em> and responsible for heartwater, a disease of domestic and wild ruminants. High genetic diversity of <em>E. ruminantium</... |  | Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Microbiology of infections | Thomas Pollet | Rodolfo García-Contreras, Alejandro Cabezas-Cruz | 2021-10-14 16:54:54 | View |
21 Jul 2022

Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV)Nurul Novelia Fuandila, Anne-Sophie Gosselin-Grenet, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sven M Bergmann, Jean-Michel Escoubas, Sandro Klafack, Angela Mariana Lusiastuti, Munti Yuhana, Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier, Jean-Christophe Avarre, Emira Cherif https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.483410Understanding the in vitro evolution of Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3), a story of structural variations that can lead to the design of attenuated virus vaccinesRecommended by Jorge Amich based on reviews by Lucie Cappuccio and Veronique Hourdel based on reviews by Lucie Cappuccio and Veronique Hourdel
Structural variations (SVs) play a key role in viral evolution, and therefore they are also important for infection dynamics. However, the contribution of structural variations to the evolution of double-stranded viruses is limited. This knowledge can help to understand the population dynamics and might be crucial for the future development of viral attenuated vaccines. In this study, Fuandila et al (1) use the Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3), commonly known as koi herpesvirus (KHV), to investigate the variability and contribution of structural variations (SV) for viral evolution after 99 passages in vitro. This virus, with the largest genome among herperviruses, causes a lethal infection in common carp and koi associated with mortalities up to 95% (2). Interestingly, KHV infections are caused by haplotype mixtures, which possibly are a source of genome diversification, but make genomic comparisons more difficult. The authors have used ultra-deep long-read sequencing of two passages, P78 and P99, which were previously described to have differences in virulence. They have found a surprisingly high and wide distribution of SVs along the genome, which were enriched in inversion and deletion events and that often led to defective viral genomes. Although it is known that these defective viral genomes negatively impact viral replication, their implications for virus persistence are still unclear. Subsequently, the authors concentrated on the virulence-relevant region ORF150, which was found to be different in P78 (deletion in 100% of the reads) and P99 (reference-like haplotype). To understand this loss and gain of full ORF150, they searched for SV turn-over in 10 intermediate passages. This analysis revealed that by passage 10 deleted and inverted (attenuated) haplotypes had already appeared, steadily increased frequency until P78, and then completely disappeared between P78 and P99. This is a striking result that raises new questions as to how this clearance occurs, which is really important as these reversions may result in undesirable increases in virulence of live-attenuated vaccines. We recommend this preprint because its use of ultra-deep long-read sequencing has permitted to better understand the role of SV diversity and dynamics in viral evolution. This study shows an unexpectedly high number of structural variations, revealing a novel source of virus diversification and confirming the different mixtures of haplotypes in different passages, including the gain of function. This research provides basic knowledge for the future design of live-attenuated vaccines, to prevent the reversion to virulent viruses. References (1) Fuandila NN, Gosselin-Grenet A-S, Tilak M-K, Bergmann SM, Escoubas J-M, Klafack S, Lusiastuti AM, Yuhana M, Fiston-Lavier A-S, Avarre J-C, Cherif E (2022) Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV). bioRxiv, 2022.03.10.483410, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.483410 (2) Sunarto A, McColl KA, Crane MStJ, Sumiati T, Hyatt AD, Barnes AC, Walker PJ. Isolation and characterization of koi herpesvirus (KHV) from Indonesia: identification of a new genetic lineage. Journal of Fish Diseases, 34, 87-101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2010.01216.x | Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV) | Nurul Novelia Fuandila, Anne-Sophie Gosselin-Grenet, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sven M Bergmann, Jean-Michel Escoubas, Sandro Klafack, Angela Mariana Lusiastuti, Munti Yuhana, Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier, Jean-Christophe Avarre, Emira Cherif | <p style="text-align: justify;">Structural variations (SVs) constitute a significant source of genetic variability in virus genomes. Yet knowledge about SV variability and contribution to the evolutionary process in large double-stranded (ds)DNA v... |  | Animal diseases, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Viruses | Jorge Amich | Lucie Cappuccio, Veronique Hourdel | 2022-03-11 10:50:50 | View |
24 Jan 2024
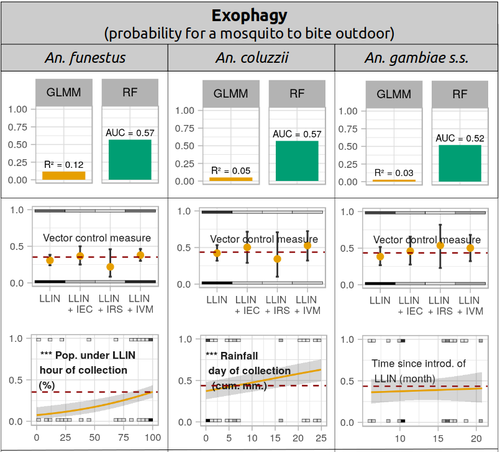
Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictabilityPaul Taconet, Dieudonné Diloma Soma, Barnabas Zogo, Karine Mouline, Frédéric Simard, Alphonsine Amanan Koffi, Roch Kounbobr Dabiré, Cédric Pennetier, Nicolas Moiroux https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.20.504631Large and complete datasets, and modelling reveal the major determinants of physiological and behavioral insecticide resistance of malaria vectorsRecommended by Thierry DE MEEÛS based on reviews by Haoues Alout and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Haoues Alout and 1 anonymous reviewer
Parasites represent the most diverse and adaptable ecological group of the biosphere (Timm & Clauson, 1988; De Meeûs et al., 1998; Poulin & Morand, 2000; De Meeûs & Renaud, 2002). The human species is known to considerably alter biodiversity, though it hosts, and thus sustains the maintenance of a spectacular diversity of parasites (179 species for eukaryotic species only) (De Meeûs et al., 2009). Among these, the five species of malaria agents (genus Plasmodium) remain a major public health issue around the world. Plasmodium falciparum is the most prevalent and lethal of these (Liu et al., 2010). With a pick of up to 2 million deaths due to malaria in 2004, deaths decreased to around 1 million in 2010 (Murray et al., 2012), to reach 619,000 in 2021, most of which in sub-Saharan Africa, and 79% of which were among children aged under 5 years (World Health Organization, 2022). As stressed by Taconet et al. (2023), reduction in malaria deaths is attributable to control measures, in particular against its vectors (mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles). Nevertheless, the success of vector control is hampered by several factors (biological, environmental and socio-economic), and in particular by the great propensity of targeted mosquitoes to evolve physiological or behavioral avoidance of anti-vectorial measures. In their paper Taconet et al. (2023) aims at understanding what are the main factors that determine the evolution of insecticide resistance in several malaria vectors, in relation to the biological determinisms of behavioral resistance and how fast such evolutions take place. To tackle these objectives, authors collected an impressive amount of data in two rural areas of West Africa. With appropriate modeling, Taconet et al. discovered, among many other results, a predominant role of public health measures, as compared to agricultural practices, in the evolution of physiological resistance. They also found that mosquito foraging activities are mostly explained by host availability and climate, with a poor, if any, association with genetic markers of physiological resistance to insecticides. These findings represent an important contribution to the field and should help at designing more efficient control strategies against malaria.
References De Meeûs T, Michalakis Y, Renaud F (1998) Santa Rosalia revisited: or why are there so many kinds of parasites in “the garden of earthly delights”? Parasitology Today, 14, 10–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4758(97)01163-0 De Meeûs T, Prugnolle F, Agnew P (2009) Asexual reproduction in infectious diseases. In: Lost Sex: The Evolutionary Biology of Parthenogenesis (eds Schön I, Martens K, van Dijk P), pp. 517-533. Springer, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2770-2_24 De Meeûs T, Renaud F (2002) Parasites within the new phylogeny of eukaryotes. Trends in Parasitology, 18, 247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-4922(02)02269-9 Liu W, Li Y, Learn GH, Rudicell RS, Robertson JD, Keele BF, Ndjango JB, Sanz CM, Morgan DB, Locatelli S, Gonder MK, Kranzusch PJ, Walsh PD, Delaporte E, Mpoudi-Ngole E, Georgiev AV, Muller MN, Shaw GM, Peeters M, Sharp PM, Rayner JC, Hahn BH (2010) Origin of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature, 467, 420–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09442 Murray CJ, Rosenfeld LC, Lim SS, Andrews KG, Foreman KJ, Haring D, Fullman N, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Lopez AD (2012) Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. The Lancet, 379, 413–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60034-8 Poulin R, Morand S (2000) The diversity of parasites. Quarterly Review of Biology, 75, 277–293. https://doi.org/10.1086/393500 Taconet P, Soma DD, Zogo B, Mouline K, Simard F, Koffi AA, Dabire RK, Pennetier C, Moiroux N (2023) Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictability. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.20.504631 Timm RM, Clauson BL (1988) Coevolution: Mammalia. In: 1988 McGraw-Hill yearbook of science & technology, pp. 212–214. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York. World Health Organization (2022) World malaria report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/365169/9789240064898-eng.pdf?sequence=1.
| Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictability | Paul Taconet, Dieudonné Diloma Soma, Barnabas Zogo, Karine Mouline, Frédéric Simard, Alphonsine Amanan Koffi, Roch Kounbobr Dabiré, Cédric Pennetier, Nicolas Moiroux | <p>Insecticide resistance and behavioural adaptation of malaria mosquitoes affect the efficacy of long-lasting insecticide nets - currently the main tool for malaria vector control. To develop and deploy complementary, efficient and cost-effective... |  | Behaviour of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Pesticide resistance, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Vectors | Thierry DE MEEÛS | Haoues Alout, Anonymous | 2023-07-03 11:29:10 | View |
06 Apr 2023

Evolution within a given virulence phenotype (pathotype) is driven by changes in aggressiveness: a case study of French wheat leaf rust populationsCécilia FONTYN, Kevin JG MEYER, Anne-Lise BOIXEL, Ghislain DELESTRE, Emma PIAGET, Corentin PICARD, Frédéric SUFFERT, Thierry C MARCEL, Henriette GOYEAU https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.29.505401Changes in aggressiveness in pathotypes of wheat leaf rustRecommended by Pierre Gladieux based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersUnderstanding the ecological and evolutionary factors underlying the spread of new fungal pathogen populations can inform the development of more effective management strategies. In plant pathology, pathogenicity is generally presented as having two components: ‘virulence’ (qualitative pathogenicity) and aggressiveness (quantitative pathogenicity). Changes in virulence in response to the deployment of new resistant varieties are a major driver of the spread of new populations (called pathotypes, or races) in modern agrosystems, and the genomic (i.e. proximal) and eco-evolutionary (i.e. ultimate) factors underlying these changes are well-documented [1,2,3]. By contrast, the role of changes in aggressiveness in the spread of pathotypes remains little known [4]. The study by Cécilia Fontyn and collaborators [5] set out to characterize changes in aggressiveness for isolates of two pathotypes of the wheat leaf rust (Puccinia triticina) that have been dominant in France during the 2005-2016 period. Isolates were genetically characterized using multilocus microsatellite typing and phenotypically characterized for three components of aggressiveness on wheat varieties: infection efficiency, latency period, and sporulation capacity. Using experiments that represent quite a remarkable amount of work and effort, Fontyn et al. showed that each dominant pathotype consisted of several genotypes, including common genotypes whose frequency changed over time. For each pathotype, the genotypes that were more common initially were replaced by a more aggressive genotype. Together, these results show that changes in the genetic composition of populations of fungal plant pathogens can be associated with, and may be caused by, changes in the quantitative components of pathogenicity. This study also illustrates how extensive, decade-long monitoring of fungal pathogen populations, such as the one conducted for wheat leaf rust in France, represents a very valuable resource for research. REFERENCES [1] Brown, J. K. (1994). Chance and selection in the evolution of barley mildew. Trends in Microbiology, 2(12), 470-475. https://doi.org/10.1016/0966-842x(94)90650-5 [2] Daverdin, G., Rouxel, T., Gout, L., Aubertot, J. N., Fudal, I., Meyer, M., Parlange, F., Carpezat, J., & Balesdent, M. H. (2012). Genome structure and reproductive behaviour influence the evolutionary potential of a fungal phytopathogen. PLoS Pathogens, 8(11), e1003020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003020 [3] Gladieux, P., Feurtey, A., Hood, M. E., Snirc, A., Clavel, J., Dutech, C., Roy, M., & Giraud, T. (2015). The population biology of fungal invasions.Molecular Ecology, 24(9), 1969-86. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13028 [4] Fontyn, C., Zippert, A. C., Delestre, G., Marcel, T. C., Suffert, F., & Goyeau, H. (2022). Is virulence phenotype evolution driven exclusively by Lr gene deployment in French Puccinia triticina populations?. Plant Pathology, 71(7), 1511-1524. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.13599 [5] Fontyn, C., Meyer, K. J., Boixel, A. L., Delestre, G., Piaget, E., Picard, C., Suffer, F., Marcel, T.C., & Goyeau, H. (2022). Evolution within a given virulence phenotype (pathotype) is driven by changes in aggressiveness: a case study of French wheat leaf rust populations. bioRxiv, 2022.08.29.505401, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.29.505401 | Evolution within a given virulence phenotype (pathotype) is driven by changes in aggressiveness: a case study of French wheat leaf rust populations | Cécilia FONTYN, Kevin JG MEYER, Anne-Lise BOIXEL, Ghislain DELESTRE, Emma PIAGET, Corentin PICARD, Frédéric SUFFERT, Thierry C MARCEL, Henriette GOYEAU | <p style="text-align: justify;">Plant pathogens are constantly evolving and adapting to their environment, including their host. Virulence alleles emerge, and then increase, and sometimes decrease in frequency within pathogen populations in respon... |  | Coevolution, Epidemiology, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Pathogenic/Symbiotic Fungi, Phytopathology, Plant diseases, Population dynamics of hosts, infectious agents, or... | Pierre Gladieux | Emerson Del Ponte , Jacqui Shykoff, Leïla Bagny Beilhe , Alexey Mikaberidze | 2022-09-29 20:01:57 | View |
29 Jan 2024
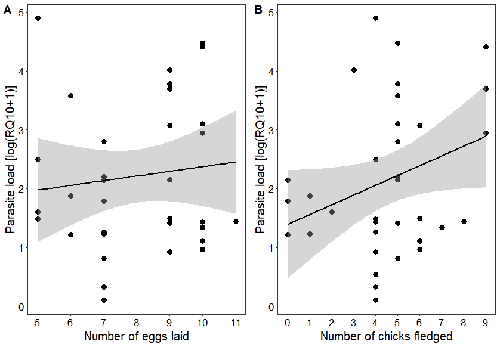
Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine birdRomain Pigeault, Camille-Sophie Cozzarolo, Jérôme Wassef, Jérémy Gremion, Marc Bastardot, Olivier Glaizot, Philippe Christe https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.28.550923Avian Plasmodium parasitaemia as an indicator of reproduction investmentRecommended by Claire Loiseau based on reviews by Luz García-Longoria and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Luz García-Longoria and 2 anonymous reviewers
Effects of the seasonal variations on within-host parasitaemia are still not well understood and potentially due to numerous factors, e.g. host and parasite species, host sex or age, or geographical regions. In this study, over three years in Switzerland, Pigeault et al. (2024) collected data on great tits reproductive outputs – laying date, clutch size, fledging success – to determine whether they were associated with avian Plasmodium parasitaemia before (winter), during (spring) and after (autumn) the breeding season. They focused on two lineages from two species: a highly generalist lineage Plasmodium relictum (lineage SGS1; Bensch et al. 2009) and a more specialized lineage Plasmodium homonucleophilum (lineage SW2). As previously found, they showed that parasitaemia level is low during the winter and then increase in spring (Applegate, 1970; Applegate 1971). Spring recurrences have been intensively studied but are still not well understood since many non-exclusive factors can provoke them, i.e environmental stressors, reproductive hormones, co-infections or bites of mosquitoes (Cornet et al. 2014). Interestingly, the parasitaemia level during the winter before and during the breeding season were not associated to the reproductive success, meaning that birds in their populations with low parasitaemia during the winter had not more fledglings than the ones with a higher parasitaemia. However, the individuals who invested the most in the reproduction with a higher number of fledglings had also a higher parasitaemia in the following autumn. The number of laid eggs was not associated with the parasitaemia during the following autumn, showing that the initial investment in the reproduction is less important than the parental care (e.g. chicks feeding) in terms of mid/long term cost. The originality here is that authors followed populations during three periods of the year, which is not an easy task and rarely done in natural populations. Their results highlight the mid/long-term effect of higher resource allocation into reproduction on individuals’ immune system and ability to control parasite replication. Further analyses on various lineages and bird populations from other geographical regions (i.e. different latitudes) would be the next relevant step. References Applegate JE (1971) Spring relapse of Plasmodium relictum infections in an experimental field population of English sparrows (Passer domesticus). Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 7, 37–42. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-7.1.37 Applegate JE, Beaudoin RL (1970) Mechanism of spring relapse in avian malaria: Effect of gonadotropin and corticosterone. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 6, 443–447. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-6.4.443 Bensch S, Hellgren O, Pérez‐Tris J (2009) MalAvi: a public database of malaria parasites and related haemosporidians in avian hosts based on mitochondrial cytochrome b lineages. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 1353-1358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02692.x Cornet S, Nicot A, Rivero A, Gandon S (2014) Evolution of plastic transmission strategies in avian malaria. PLoS Pathogens, 10, e1004308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004308 Pigeault R, Cozzarolo CS, Wassef J, Gremion J, Bastardot M, Glaizot O, Christe P (2024) Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine bird. bioRxiv ver 3. Peer reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.28.550923 | Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine bird | Romain Pigeault, Camille-Sophie Cozzarolo, Jérôme Wassef, Jérémy Gremion, Marc Bastardot, Olivier Glaizot, Philippe Christe | <p>Although avian haemosporidian parasites are widely used as model organisms to study fundamental questions in evolutionary and behavorial ecology of host-parasite interactions, some of their basic characteristics, such as seasonal variations in ... |  | Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Parasites | Claire Loiseau | Carolina Chagas, Anonymous, Luz García-Longoria | 2023-08-11 14:14:56 | View |
23 Jan 2023

Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolenseMoana Peylhard, David Berthier, Guiguigbaza-Kossigan Dayo, Isabelle Chantal, Souleymane Sylla, Sabine Nidelet, Emeric Dubois, Guillaume Martin, Guilhem Sempéré, Laurence Flori, Sophie Thévenon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.10.495622Whole genome transcriptome reveals metabolic and immune susceptibility factors for Trypanosoma congolense infection in West-African livestockRecommended by Concepción Marañón based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersAfrican trypanosomiasis is caused by to the infection of a protozoan parasite of the Trypanosoma genus. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly, and is largely affecting cattle in the sub-humid areas of Africa, causing a high economic impact. However, not all the bovine strains are equally susceptible to the infection (1). In order to dissect the mechanisms underlying susceptibility to African trypanosoma infection, Peylhard et al (2) performed blood transcriptional profiles of trypanotolerant, trypanosensitive and mixed cattle breeds, before and after experimental infection with T. congolense. First of all, the authors have characterized the basal transcriptional profiles in the blood of the different breeds under study, which could be classified in a wide array of functional pathways. Of note, after infection some pathways were consistently enriched in all the group tested. Among them, the immune system-related ones were again on the top functions reported. The search for specific canonical pathways pointed to a prominent role of lipid and cholesterol-related pathways, as well as mitochondrial function and B and T lymphocyte activation. However, the analysis of infected animals demonstrated that trypanosusceptible animals showed a stronger transcriptomic reprogramming, highly enriched in specific metabolic and immunological pathways. It is worthy to highlight striking differences in genes involved in immune signal transduction, cytokines and markers of different leukocyte subpopulations. This work represents undoubtedly a significant momentum in the field, since the authors explore in deep a wide panel of cattle breeds representing the majority of West-African taurine and zebu in a systematic way. Since the animals were studied at different timepoints after infection, future longitudinal analyses of these datasets will be providing a precious insight on the kinetics of immune and metabolic reprogramming associated with susceptibility and tolerance to African trypanosoma infection, widening the application of this interesting study into new therapeutic interventions. References 1. Berthier D, Peylhard M, Dayo G-K, Flori L, Sylla S, Bolly S, Sakande H, Chantal I, Thevenon S (2015) A Comparison of Phenotypic Traits Related to Trypanotolerance in Five West African Cattle Breeds Highlights the Value of Shorthorn Taurine Breeds. PLOS ONE, 10, e0126498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126498 2. Peylhard M, Berthier D, Dayo G-K, Chantal I, Sylla S, Nidelet S, Dubois E, Martin G, Sempéré G, Flori L, Thévenon S (2022) Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolense. bioRxiv, 2022.06.10.495622, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.10.495622. | Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolense | Moana Peylhard, David Berthier, Guiguigbaza-Kossigan Dayo, Isabelle Chantal, Souleymane Sylla, Sabine Nidelet, Emeric Dubois, Guillaume Martin, Guilhem Sempéré, Laurence Flori, Sophie Thévenon | <p>Animal African trypanosomosis, caused by blood protozoan parasites transmitted mainly by tsetse flies, represents a major constraint for millions of cattle in sub-Saharan Africa. Exposed cattle include trypanosusceptible indicine breeds, severe... |  | Animal diseases, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Resistance/Virulence/Tolerance | Concepción Marañón | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-06-14 17:06:57 | View |
08 Aug 2023
A global Corynebacterium diphtheriae genomic framework sheds light on current diphtheria reemergenceMelanie Hennart, Chiara Crestani, Sebastien Bridel, Nathalie Armatys, Sylvie Brémont, Annick Carmi-Leroy, Annie Landier, Virginie Passet, Laure Fonteneau, Sophie Vaux, Julie Toubiana, Edgar Badell, Sylvain Brisse https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.20.529124DIPHTOSCAN : A new tool for the genomic surveillance of diphtheriaRecommended by Rodolfo García-Contreras based on reviews by Ankur Mutreja and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the greatest achievements of health sciences is the eradication of infectious diseases such as smallpox that in the past imposed a severe burden on humankind, through global vaccination campaigns. Moreover, progress towards the eradication of others such as poliomyelitis, dracunculiasis, and yaws is being made. In contrast, other infections that were previously contained are reemerging, due to several factors, including lack of access to vaccines due to geopolitical reasons, the rise of anti-vaccine movements, and the constant mobility of infected persons from the endemic sites. One of such disease is diphtheria, caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae and a few other related species such as C. ulcerans and C. pseudotuberculosis. Importantly, in France, diphtheria cases reported in 2022 increased 7-fold from the average of previously recorded cases per year in the previous 4 years and the situation in other European countries is similar. Hence, as reported here, Hennart et al. (2023) developed DIPHTOSCAN, a free access bioinformatics tool with user-friendly interphase, aimed to easily identify, extract and interpret important genomic features such as the sublineage of the strain, the presence of the tox gene (as a string predictor for toxigenic disease) as well as genes coding other virulence factors such as fimbriae, and the presence of know resistant mechanisms towards antibiotics like penicillin and erythromycin currently used in the clinic to treat this infection. The authors validated the performance of their tool with a large collection of genomes, including those obtained from the isolates of the 2022 outbreak in France, more than 1,200 other genomes isolated from France, Algeria, and Yemen, and more than 500 genomes from several countries from Europe, America, Africa, Asia, and Oceania that are available through the NCBI site. DIPHTOSCAN will allow the rapid identification and surveillance of potentially dangerous strains such as those being tox-positive isolates and resistant to multiple drugs and/or first-line treatments and a better understanding of the epidemiology and evolution of this important reemerging disease. | A global *Corynebacterium diphtheriae* genomic framework sheds light on current diphtheria reemergence | Melanie Hennart, Chiara Crestani, Sebastien Bridel, Nathalie Armatys, Sylvie Brémont, Annick Carmi-Leroy, Annie Landier, Virginie Passet, Laure Fonteneau, Sophie Vaux, Julie Toubiana, Edgar Badell, Sylvain Brisse | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background</strong></p> <p style="text-align: justify;">Diphtheria, caused by <em>Corynebacterium diphtheriae</em>, reemerges in Europe since 2022. Genomic sequencing can inform on transmission routes and g... | Drug resistance, tolerance and persistence, Epidemiology, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Microbiology of infections, Population genetics of hosts, infectiou... | Rodolfo García-Contreras | Ankur Mutreja | 2023-03-09 16:02:27 | View | |
08 Dec 2022
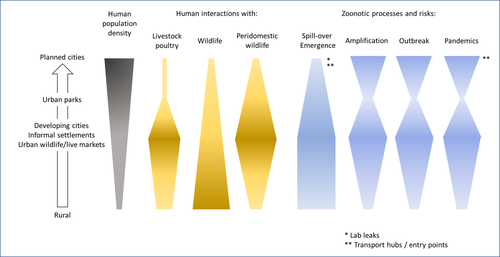
Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystemsDobigny, G. & Morand, S. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776Zoonotic emergence and the overlooked case of citiesRecommended by Etienne Waleckx based on reviews by Eric Dumonteil, Nicole L. Gottdenker and 1 anonymous reviewerZoonotic pathogens, those transmitted from animals to humans, constitute a major public health risk with high associated global economic costs. Diseases associated with these pathogens represent more than 60% of emerging infectious diseases and predominantly originate in wildlife (1). Over the last decades, the emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic pathogens have led to an increasing number of epidemics, as illustrated by the current Covid-19 pandemic. There is ample evidence that human impact on native ecosystems such as deforestation, agricultural development, and urbanization, is linked to spillover of pathogens from animals to humans (2). However, research and calls to action have mainly focused on the importance of surveillance and prevention of zoonotic emergences along landscape interfaces, with special emphasis on tropical forests and agroecosystems, and studies and reviews pointing out the zoonotic risk associated with cities are scarce. Additionally, cities are sometimes wrongly seen as one homogeneous ecosystem, almost exclusively human, with a Northern hemisphere-biased perception of what a city is, which fails to take into account the ecological and socio-economic diversities that can constitute an urban area. Here, Dobigny and Morand (3) aim to draw attention to the importance of urban ecosystems in zoonotic risk and advocate that further attention should be paid to urban, peri-urban and suburban areas. In this well-organized and well-documented review, the authors show, using updated literature, that cities are places where massive contacts occur between wildlife, domestic animals, and human inhabitants (thus constituting spillover opportunities), and that it is even likely that human and wildlife contact in urban centers is more prevalent than in wild areas, perhaps contrary to intuition. Indeed, cities currently constitute the most important environment of human life and are places for millions of close interactions between humans and animals, including pets and domestic animals, wild animals through the intrusion of wild urban-adapted species (e.g., some bat, rodent, or bird species among others), manipulation and consumption of wildlife meat, and the existence of wildlife meat markets, which all constitute a major risk for zoonotic spillover. In cities, lab escapees of zoonotic pathogens also exist, and trends of adaptation to urban ecological conditions of many vectors of primary health importance is also a concern. The authors further argue that cities are predominant places for both epidemic amplification of human-human transmitted pathogens, because they are places with high human densities and population growth, and for dissemination of reservoirs, vectors and pathogens, as they are transport hubs. Dobigny & Morand further predict, likely correctly, that cities may be important places for pathogen evolution. Finally, they propose actions and recommendations to limit the risk of zoonotic spillover events from urban ecosystems and future directions for research aiming at assessing this risk. The reviewers found the manuscript well-organized and presented, timely, and bringing novel contributions to the field of zoonotic emergence. I strongly recommend this article, which should benefit a large audience, particularly in the context of the current Covid-19 pandemics and the ongoing One Health initiatives aiming at preventing future zoonotic disease emergence (4). References (1) Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451, 990–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06536 (2) White RJ, Razgour O (2020) Emerging zoonotic diseases originating in mammals: a systematic review of effects of anthropogenic land-use change. Mammal Review, 50, 336–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/mam.12201 (3) Dobigny G, Morand S (2022) Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems. Zenodo, 6444776, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776 (4) Morand S, Lajaunie C (2021) Biodiversity and COVID-19: A report and a long road ahead to avoid another pandemic. One Earth, 4, 920–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.06.007 | Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems | Dobigny, G. & Morand, S. | <p style="text-align: justify;">Zoonotic emergence requires spillover from animals to humans, hence animal-human interactions. A lot has been emphasized on human intrusion into wild habitats (e.g., deforestation, hunting) and the development of ag... |  | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, One Health, Zoonoses | Etienne Waleckx | 2022-04-11 11:39:11 | View | |
28 Oct 2022

Development of nine microsatellite loci for Trypanosoma lewisi, a potential human pathogen in Western Africa and South-East Asia, and preliminary population genetics analysesAdeline Ségard, Audrey Romero, Sophie Ravel, Philippe Truc, Gauthier Dobigny, Philippe Gauthier, Jonas Etougbetche, Henri-Joel Dossou, Sylvestre Badou, Gualbert Houéménou, Serge Morand, Kittipong Chaisiri, Camille Noûs, Thierry deMeeûs https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6460010Preliminary population genetic analysis of Trypanosoma lewisiRecommended by Annette MacLeod based on reviews by Gabriele Schönian and 1 anonymous reviewerTrypanosoma lewisi is an atypical trypanosome species. Transmitted by fleas, it has a high prevalence and worldwide distribution in small mammals, especially rats [1]. Although not typically thought to infect humans, there has been a number of reports of human infections by T. lewisi in Asia including a case of a fatal infection in an infant [2]. The fact that the parasite is resistant to lysis by normal human serum [3] suggests that many people, especially immunocompromised individuals, may be at risk from zoonotic infections by this pathogen, particularly in regions where there is close contact with T. lewisi-infected rat fleas. Indeed, it is also possible that cryptic T. lewisi infections exist but have hitherto gone undetected. Such asymptomatic infections have been detected for a number of parasitic infections including the related parasite T. b. gambiense [4]. References
[2] Truc P, Büscher P, Cuny G, Gonzatti MI, Jannin J, Joshi P, Juyal P, Lun Z-R, Mattioli R, Pays E, Simarro PP, Teixeira MMG, Touratier L, Vincendeau P, Desquesnes M (2013) Atypical Human Infections by Animal Trypanosomes. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 7, e2256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002256 [3] Lun Z-R, Wen Y-Z, Uzureau P, Lecordier L, Lai D-H, Lan Y-G, Desquesnes M, Geng G-Q, Yang T-B, Zhou W-L, Jannin JG, Simarro PP, Truc P, Vincendeau P, Pays E (2015) Resistance to normal human serum reveals Trypanosoma lewisi as an underestimated human pathogen. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 199, 58–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molbiopara.2015.03.007 [4] Büscher P, Bart J-M, Boelaert M, Bucheton B, Cecchi G, Chitnis N, Courtin D, Figueiredo LM, Franco J-R, Grébaut P, Hasker E, Ilboudo H, Jamonneau V, Koffi M, Lejon V, MacLeod A, Masumu J, Matovu E, Mattioli R, Noyes H, Picado A, Rock KS, Rotureau B, Simo G, Thévenon S, Trindade S, Truc P, Reet NV (2018) Do Cryptic Reservoirs Threaten Gambiense-Sleeping Sickness Elimination? Trends in Parasitology, 34, 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2017.11.008 [5] Ségard A, Roméro A, Ravel S, Truc P, Gauthier D, Gauthier P, Dossou H-J, Sylvestre B, Houéménou G, Morand S, Chaisiri K, Noûs C, De Meeûs T (2022) Development of nine microsatellite loci for Trypanosoma lewisi, a potential human pathogen in Western Africa and South-East Asia, and preliminary population genetics analyses. Zenodo, 6460010, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6460010 | Development of nine microsatellite loci for Trypanosoma lewisi, a potential human pathogen in Western Africa and South-East Asia, and preliminary population genetics analyses | Adeline Ségard, Audrey Romero, Sophie Ravel, Philippe Truc, Gauthier Dobigny, Philippe Gauthier, Jonas Etougbetche, Henri-Joel Dossou, Sylvestre Badou, Gualbert Houéménou, Serge Morand, Kittipong Chaisiri, Camille Noûs, Thierry deMeeûs | <p><em>Trypanosoma lewisi</em> belongs to the so-called atypical trypanosomes that occasionally affect humans. It shares the same hosts and flea vector of other medically relevant pathogenic agents as Yersinia pestis, the agent of plague. Increasi... |  | Animal diseases, Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Eukaryotic pathogens/symbionts, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Microbiology of infections, Parasites, Population genetics of hosts, in... | Annette MacLeod | 2022-04-21 17:04:37 | View | |
07 Feb 2023
Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populationsMarie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084Unveiling the complex interactions between members of gut microbiomes: a significant advance provided by an exhaustive study of wild bank volesRecommended by Thomas Pollet based on reviews by Jason Anders and 1 anonymous reviewerThe gut of vertebrates is a host for hundreds or thousands of different species of microorganisms named the gut microbiome. This latter may differ greatly in natural environments between individuals, populations and species (1). The vertebrate gut microbiome plays key roles in host fitness through functions including nutrient acquisition, immunity and defense against infectious agents. While bank voles are small mammals potentially reservoirs of a large number of infectious agents, questions about the links between their gut microbiome and the presence of pathogens are scarcely addressed. In this study, Bouilloud et al. (2) used complementary analyses of community and microbial ecology to (i) assess the variability of gut bacteriome diversity and composition in wild populations of the bank vole Myodes glareolus collected in four different sites in Eastern France and (ii) evaluate the three-way interactions between the gut bacteriota, the gastro-intestinal helminths and pathogenic bacteria detected in the spleen. Authors identified important variations of the gut bacteriota composition and diversity among bank voles mainly explained by sampling localities. They found positive correlations between the specific richness of both the gut bacteria and the helminth community, as well as between the composition of these two communities, even when accounting for the influence of geographical distance. The helminths Aonchotheca murissylvatici, Heligmosomum mixtum and the bacteria Bartonella sp were the main taxa associated with the whole gut bacteria composition. Besides, changes in relative abundance of particular gut bacterial taxa were specifically associated with other helminths (Mastophorus muris, Catenotaenia henttoneni, Paranoplocephala omphalodes and Trichuris arvicolae) or pathogenic bacteria. Infections with Neoehrlichia mikurensis, Orientia sp, Rickettsia sp and P. omphalodes were especially associated with lower relative abundance of members of the family Erysipelotrichaceae (Firmicutes), while coinfections with higher number of bacterial infections were associated with lower relative abundance of members of the Bacteroidales family (Bacteroidetes). As pointed out by both reviewers, this study represents a significant advance in the field. I would like to commend the authors for this enormous work. The amount of data, analyses and results is considerable which has sometimes complicated the understanding of the story at the beginning of the evaluation process. Thanks to constructive scientific interactions with both reviewers through the two rounds of evaluation, the authors have efficiently addressed the reviewer's concerns and improved the manuscript, making this great story easier to read. The innovative results of this study emphasize the complex interlinkages between gut bacteriome and infections in wild animal populations and I strongly recommend this article for publication In Peer Community Infections. References (1) Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Sklar J, Jiang L, Natarajan L, Knight R, Belkaid Y (2020) Host variables confound gut microbiota studies of human disease. Nature, 587, 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2881-9 (2) Bouilloud M, Galan M, Dubois A, Diagne C, Marianneau P, Roche B, Charbonnel N (2023) Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations. biorxiv, 2022.05.23.493084, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084 | Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations | Marie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel | <p>Background</p> <p>Despite its central role in host fitness, the gut microbiota may differ greatly between individuals. This variability is often mediated by environmental or host factors such as diet, genetics, and infections. Recently, a part... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Reservoirs, Zoonoses | Thomas Pollet | 2022-05-25 10:13:23 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Jorge Amich
Christine Chevillon
Fabrice Courtin
Christine Coustau
Thierry De Meeûs
Heather R. Jordan
Karl-Heinz Kogel
Yannick Moret
Thomas Pollet
Benjamin Roche
Benjamin Rosenthal
Bashir Salim
Lucy Weinert










