Latest recommendations

| Id▼ | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
16 Jul 2024
Diverse fox circovirus (Circovirus canine) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (Canis lupus) from the Northwest Territories, CanadaMarta Canuti, Abigail V.L. King, Giovanni Franzo, H. Dean Cluff, Lars E. Larsen, Heather Fenton, Suzanne C. Dufour, Andrew S. Lang https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.08.584028Wild canine viruses in the news. Better understanding multi-host transmission by adopting a disease ecology species community-based approachRecommended by Jean-Francois Guégan based on reviews by Arvind Varsani and 1 anonymous reviewerAccording to the international animal health authority, i.e., the World Organization on Animal Health (WOAH, former OIE), circoviruses are part of the Circoviridae family, which only includes 2 genera Circovirus and Cyclovirus, and infect swine, canine, ursid, viverrid, felid, pinniped, herpestid, mustelid, and several avian species (WOAH 2021). They are small (12–27 nm), non-enveloped, circular, single-stranded DNA viruses, viral replication is nuclear, and wild and domestic birds and mammals could serve as natural hosts. If most infections caused by circoviruses are subclinical in both wild and domestic species, they can be responsible for severe diseases in the commercial pig industry due to the Porcine circovirus-2 (PCV-2). These viruses can constitute a threat to wildlife, and cause their hosts to become immunocompromised, and animals often present with secondary coinfections. Canine circoviruses (CanineCV) harbour a worldwide distribution in dogs, and is the sole member of the viral genus to infect canines. They can be detected in wild carnivores, such as wolves, badgers, foxes and jackals, which indicates an ability for cross-species transmission between wildlife and domestic dogs. However, fox circovirus (FoCV), a distinct lineage of CanineCV, has been identified exclusively in wild canids (foxes and wolves) and not in dogs in Europe and North America, where it can cause in red foxes meningoencephalitis and other central nervous system signs. In their article, Canuti et al. (2024) investigate the presence, distribution and ecology of CanineCV in grey wolf specimens from the Northwest Territories, Canada. CanineCV occurrence appears to be relatively high with 45.3% positive specimens and parvoviral superinfections observed. The authors identify a high CanineCV genetic diversity among the investigated grey wolf specimens, and exacerbated by viral recombination. Phylogenetic analysis reveals the existence of 4 lineages, within each of them strains segregate by geography and not by host origin. This observed geographic segregation is interpreted as being due to the absence of exchange flows between grey wolf host subpopulations. Due to the paucity of knowledge on these circoviruses in wildlife and at the interface between wild and domestic animals, the authors discuss the plausible role of wolves as natural host reservoirs for disease transmission due to long-lasting virus-host coevolution. They are also conscious that additional maintenance hosts could exist in the wild, claiming for further studies to decipher fox circovirus disease ecology and transmission dynamics. This study underlines the importance of better understanding the transmission ecology and evolution of these Canine circoviruses, and I can only agree. Xiao et al. (2023), a research not referred to in the present work, evidenced CanineCV infection in cats in China, and obtained the first whole genome of cat-derived CanineCV. This emphasizes the importance of monitoring additional animal species and locations in the world to clarify disease ecology and transmission dynamics. A broader sampling of a wide range of animal species in different parts of the world using a species community-based approach is the key to understanding these CanineCV infections. References Marta CANUTI, Abigail V.L. KING, Giovanni FRANZO, H. Dean CLUFF, Lars E. LARSEN, Heather FENTON, Suzanne C. DUFOUR, Andrew S. LANG. 2024. Diverse fox circovirus (Circovirus canine) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (Canis lupus) from the Northwest Territories, Canada. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.08.584028 World Organization on Animal Health. 2021. Circoviruses. https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/05/circoviruses-infection-with.pdf [consulted on July 9th, 2024]. Xiangyu XIAO, Yan CHAO LI, Feng PEI XU, Xiangpi HAO, Shoujun LI, Pei ZHOU. 2023. Canine circovirus among dogs and cats in China: first identification in cats. Front. Microbiol. 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1252272 | Diverse fox circovirus (*Circovirus canine*) variants circulate at high prevalence in grey wolves (*Canis lupus*) from the Northwest Territories, Canada | Marta Canuti, Abigail V.L. King, Giovanni Franzo, H. Dean Cluff, Lars E. Larsen, Heather Fenton, Suzanne C. Dufour, Andrew S. Lang | <p style="text-align: justify;">Canine circoviruses (CanineCV) have a worldwide distribution in dogs and are occasionally detected in wild carnivorans, indicating their ability for cross-species transmission. However, fox circovirus, a lineage of ... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Epidemiology, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Reservoirs, Taxonomy of hosts, infec... | Jean-Francois Guégan | Martine Peeters, Arvind Varsani | 2024-03-09 09:04:29 | View | |
24 Jun 2024
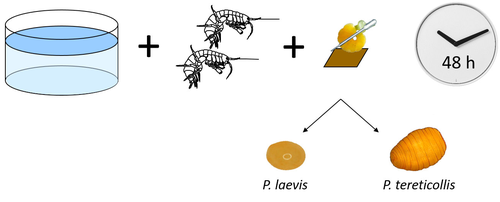
Differences in specificity, development time and virulence between two acanthocephalan parasites, infecting two cryptic species of Gammarus fossarumAlexandre Bauer, Lucie Develay Nguyen, Sébastien Motreuil, Maria Teixeira, Nelly Debrosse, Thierry Rigaud https://hal.science/hal-04455823Gammarid is not equal gammarid for acanthocephalan parasitesRecommended by Daniel Grabner based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe question on the role of different alternative hosts in the life cycle of acanthocephalan parasites has not been fully resolved to date. There is some information on the use of fish hosts in the genus Pomphorhynchus (Perrot-Minnot et al. 2019). It is known that acanthocephalans of the genus Pomphorhynchus can infect a number of different amphipod species (e.g. Bauer et al. 2000; Cornet et al. 2010; Dezfuli et al. 1999) but it is not clear if some host species might be more “advantageous” for the parasite, or if the parasite is more virulent to some host species than to others. Bauer et al. (2024) investigated different well characterized cryptic lineages of Gammarus fossarum (Weiss et al. 2013) for their susceptibility for two Pomphorhynchus sp. The results show that there is a difference in susceptibility to acanthocephalans between different linages of G. fossarum. Additionally, a parasite species specific difference was detected: the difference in susceptibility was more pronounced for P. tereticollis than for P. laevis. P. tereticollis was less virulent and developed slower than P. laevis (in G. fossarum). Besides the improved understanding of the biology of acanthocephalan parasites, this study clearly points out that we have to be careful with putting the “generalist” label on parasites simply due to the number of alternative host species we find them in. Instead, we should always have in mind that some of these hosts might be less suitable for the parasite than others when comparing quantitative data on the infection success. I highly appreciate the experimental approach taken that allows more profound conclusions than evaluations of field data. Experiments and analyses have been conducted well. I think this paper is significantly enhancing our knowledge on the specificity for the intermediate host. I find it highly remarkable that this was even found among different host lineages. References Bauer, A., Trouve, S., Gregoire, A., Bollache, L., Cezilly, F. (2000) Differential influence of Pomphorhynchus laevis (Acanthocephala) on the behaviour of native and invader gammarid species. International Journal for Parasitology, 30(14), 1453-1457. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(00)00138-7 Bauer, A., Develay Nguyen, L., Motreuil, S., Teixeira, M., Debrosse, N., Rigaud, T. (2024) Experimental infections reveal differences in specificity, development time and virulence between the acanthocephalan parasite Pomphorhynchus tereticollis and its sympatric counterpart P. laevis, in two cryptic species of Gammarus fossarum. HAL, Ver. 2, Peer-Reviewed and Recommended by Peer Community in Infections, hal-04455823. https://hal.science/hal-04455823 Cornet, S., Sorci, G., Moret, Y. (2010) Biological invasion and parasitism: invaders do not suffer from physiological alterations of the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis. Parasitology, 137(1), 137-147. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182009991077 Dezfuli, B.S., Rossetti, E., Bellettato, C.M., Maynard, B.J. (1999) Pomphorhynchus laevis in its intermediate host Echinogammarus stammeri in the River Brenta, Italy. Journal of Helminthology, 73(2), 95-102. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X00700277 Perrot-Minnot, M.J., Guyonnet, E., Bollache, L., Lagrue, C. (2019) Differential patterns of definitive host use by two fish acanthocephalans occurring in sympatry: Pomphorhynchus laevis and Pomphorhynchus tereticollis. International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife, 8, 135-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.01.007 Weiss, M., Macher, J.N., Seefeldt, M.A., Leese, F. (2013) Molecular evidence for further overlooked species within the Gammarus fossarum complex (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Hydrobiologia, 721(1), 165-184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1658-7
| Differences in specificity, development time and virulence between two acanthocephalan parasites, infecting two cryptic species of *Gammarus fossarum* | Alexandre Bauer, Lucie Develay Nguyen, Sébastien Motreuil, Maria Teixeira, Nelly Debrosse, Thierry Rigaud | <p style="text-align: justify;">Multi-host parasites can exploit various host species that differ in abundance and susceptibility to infection, which will contribute unequally to their transmission and fitness. Several species of acanthocephalan m... |  | Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Resistance/Virulen... | Daniel Grabner | 2024-02-14 13:39:19 | View | |
14 Feb 2024
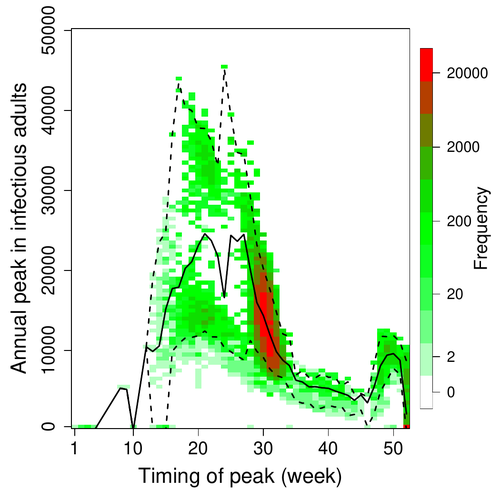
A Bayesian analysis of birth pulse effects on the probability of detecting Ebola virus in fruit batsDavid R.J. Pleydell, Innocent Ndong Bass, Flaubert Auguste Mba Djondzo, Dowbiss Meta Djomsi, Charles Kouanfack, Martine Peeters, Julien Cappelle https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.10.552777Epidemiological modeling to optimize the detection of zoonotic viruses in wild (reservoir) speciesRecommended by Aurelien Tellier based on reviews by Hetsron Legrace NYANDJO BAMEN and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Hetsron Legrace NYANDJO BAMEN and 1 anonymous reviewer
Various species of Ebolavirus have caused, and are still causing, zoonotic outbreaks and public health crises in Africa. Bats have long been hypothesized to be important reservoir populations for a series of viruses such as Hendra or Marburg viruses, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2) as well as Ebolaviruses [2, 3]. However the ecology of disease dynamics, disease transmission, and coevolution with their natural hosts of these viruses is still poorly understood, despite their importance for predicting novel outbreaks in human or livestock populations. The evidence that bats function as sylvatic reservoirs for Ebola viruses is yet only partial. Indeed, only few serological studies demonstrated the presence of Ebolavirus antibodies in young bats [4], albeit without providing positive controls of viral detection or identifying the viral species (via PCR). There is thus an unexplained discrepancy between serological data and viral detection [2, 4]. In this article, Pleydell et al. [1] use a modeling approach as well as published serological and age-structure (of the bat population) data to calibrate the model simulations. The study starts with the development of an age-structured epidemiological model which includes seasonal birth pulses and waning immunity, both generating pulses of Ebolavirus transmission within a colony of African straw-coloured fruit bats (Eidolon helvum). The epidemiological dynamics of such system of ordinary differential equations can generate annual outbreaks, skipped years or multi-annual cycles up to chaotic dynamics. Therefore, the calibration of the parameters, and the definition of biologically relevant priors, are key. To this aim, the serological data are obtained from a previous study in Cameroon [5], and the age structured of the bat population (birth and mortality) from a population study in Ghana [6]. These data are integrated into the Bayesian analysis and statistical framework to fit the model and generate predictions. In a nutshell, the authors show an overlap between the data and credibility intervals generated by the calibrated model, which thus explains well the seasonality of age-structure, namely changes in pup presence, number of lactating females, or proportion of juveniles in May. The authors can estimate that 76% of adults and 39% of young bats do survive each year, and infections are expected to last one and a half weeks. The epidemiological model predicts that annual birth pulses likely generate annual disease outbreaks, so that weeks 30 to 31 of each year, are predicted to be the best period to isolate the circulating Ebolavirus in this bat population. From the model predictions, the authors estimate the probability to have missed an infectious bat among all the samples tested by PCR being approximately of one per two thousands. The disease dynamics pattern observed in the serology data, and replicated by the model, is likely driven by seasonal pulses of young susceptible bats entering the population. This seasonal birth event increases the viral transmission, resulting in the observed peak of viral prevalence. With the inclusion of immunity waning and antibody persistence, the model results illuminate therefore why previous studies have detected only few positive cases by PCR tests, in contrast to the evidence from serological data. This study provides a first proof of principle that epidemiological modeling, despite its many simplifying assumptions, can be applied to wild species reservoirs of zoonotic diseases in order to optimize the design of field studies to detect viruses. Furthermore, such models can contribute to assess the probability and timing of zoonotic outbreaks in human or livestock populations. This article illustrates one of the manifold applications of mathematical theory of disease epidemiology to optimize sampling of pathogens/parasites or vaccine development and release [7, 8]. The further coupling of such models with population genetics theory and statistical inference methods (using parasite genome data) increasingly provide insights into the adaptation and evolution of parasites to human, crops and livestock populations [9, 10].
References [1] Pleydell D.R.J., Ndong Bass I., Mba Djondzo F.A., Djomsi D.M., Kouanfack C., Peeters M., and J. Cappelle. 2023. A Bayesian analysis of birth pulse effects on the probability of detecting Ebola virus in fruit bats. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.10.552777 [2] Caron A., Bourgarel M., Cappelle J., Liégeois F., De Nys H.M., and F. Roger. 2018. Ebola virus maintenance: if not (only) bats, what else? Viruses 10, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/v10100549 [3] Letko M., Seifert S.N., Olival K.J., Plowright R.K., and V.J. Munster. 2020. Bat-borne virus diversity, spillover and emergence. Nature Reviews Microbiology 18, 461–471. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0394-z [4] Leroy E.M., Kumulungui B., Pourrut X., Rouquet P., Hassanin A., Yaba P., Délicat A., Paweska J.T., Gonzalez J.P., and R. Swanepoel. 2005. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature 438, 575–576. https://doi.org/10.1038/438575a [5] Djomsi D.M. et al. 2022. Dynamics of antibodies to Ebolaviruses in an Eidolon helvum bat colony in Cameroon. Viruses 14, 560. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030560 [6] Peel A.J. et al. 2016. Bat trait, genetic and pathogen data from large-scale investigations of African fruit bats Eidolon helvum. Scientific data 3, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.49 [7] Nyandjo Bamen H.L., Ntaganda J.M., Tellier A. and O. Menoukeu Pamen. 2023. Impact of imperfect vaccine, vaccine trade-off and population turnover on infectious disease dynamics. Mathematics, 11(5), p.1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11051240 [8] Saadi N., Chi Y.L., Ghosh S., Eggo R.M., McCarthy C.V., Quaife M., Dawa J., Jit M. and A. Vassall. 2021. Models of COVID-19 vaccine prioritisation: a systematic literature search and narrative review. BMC medicine, 19, pp.1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-021-02190-3 [9] Maerkle, H., John S., Metzger, L., STOP-HCV Consortium, Ansari, M.A., Pedergnana, V. and Tellier, A., 2023. Inference of host-pathogen interaction matrices from genome-wide polymorphism data. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.06.547816. [10] Gandon S., Day T., Metcalf C.J.E. and B.T. Grenfell. 2016. Forecasting epidemiological and evolutionary dynamics of infectious diseases. Trends in ecology & evolution, 31(10), pp.776-788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.07.010 | A Bayesian analysis of birth pulse effects on the probability of detecting Ebola virus in fruit bats | David R.J. Pleydell, Innocent Ndong Bass, Flaubert Auguste Mba Djondzo, Dowbiss Meta Djomsi, Charles Kouanfack, Martine Peeters, Julien Cappelle | <p>Since 1976 various species of Ebolavirus have caused a series of zoonotic outbreaks and public health crises in Africa. Bats have long been hypothesised to function as important hosts for ebolavirus maintenance, however the transmission ecology... |  | Animal diseases, Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Epidemiology, Population dynamics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Reservoirs, Viruses, Zoonoses | Aurelien Tellier | 2023-08-16 16:57:05 | View | |
29 Jan 2024
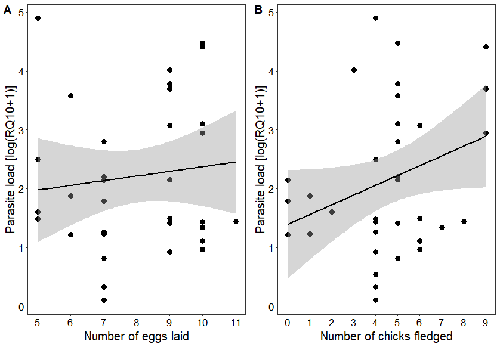
Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine birdRomain Pigeault, Camille-Sophie Cozzarolo, Jérôme Wassef, Jérémy Gremion, Marc Bastardot, Olivier Glaizot, Philippe Christe https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.28.550923Avian Plasmodium parasitaemia as an indicator of reproduction investmentRecommended by Claire Loiseau based on reviews by Luz García-Longoria and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Luz García-Longoria and 2 anonymous reviewers
Effects of the seasonal variations on within-host parasitaemia are still not well understood and potentially due to numerous factors, e.g. host and parasite species, host sex or age, or geographical regions. In this study, over three years in Switzerland, Pigeault et al. (2024) collected data on great tits reproductive outputs – laying date, clutch size, fledging success – to determine whether they were associated with avian Plasmodium parasitaemia before (winter), during (spring) and after (autumn) the breeding season. They focused on two lineages from two species: a highly generalist lineage Plasmodium relictum (lineage SGS1; Bensch et al. 2009) and a more specialized lineage Plasmodium homonucleophilum (lineage SW2). As previously found, they showed that parasitaemia level is low during the winter and then increase in spring (Applegate, 1970; Applegate 1971). Spring recurrences have been intensively studied but are still not well understood since many non-exclusive factors can provoke them, i.e environmental stressors, reproductive hormones, co-infections or bites of mosquitoes (Cornet et al. 2014). Interestingly, the parasitaemia level during the winter before and during the breeding season were not associated to the reproductive success, meaning that birds in their populations with low parasitaemia during the winter had not more fledglings than the ones with a higher parasitaemia. However, the individuals who invested the most in the reproduction with a higher number of fledglings had also a higher parasitaemia in the following autumn. The number of laid eggs was not associated with the parasitaemia during the following autumn, showing that the initial investment in the reproduction is less important than the parental care (e.g. chicks feeding) in terms of mid/long term cost. The originality here is that authors followed populations during three periods of the year, which is not an easy task and rarely done in natural populations. Their results highlight the mid/long-term effect of higher resource allocation into reproduction on individuals’ immune system and ability to control parasite replication. Further analyses on various lineages and bird populations from other geographical regions (i.e. different latitudes) would be the next relevant step. References Applegate JE (1971) Spring relapse of Plasmodium relictum infections in an experimental field population of English sparrows (Passer domesticus). Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 7, 37–42. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-7.1.37 Applegate JE, Beaudoin RL (1970) Mechanism of spring relapse in avian malaria: Effect of gonadotropin and corticosterone. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 6, 443–447. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-6.4.443 Bensch S, Hellgren O, Pérez‐Tris J (2009) MalAvi: a public database of malaria parasites and related haemosporidians in avian hosts based on mitochondrial cytochrome b lineages. Molecular Ecology Resources, 9, 1353-1358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-0998.2009.02692.x Cornet S, Nicot A, Rivero A, Gandon S (2014) Evolution of plastic transmission strategies in avian malaria. PLoS Pathogens, 10, e1004308. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004308 Pigeault R, Cozzarolo CS, Wassef J, Gremion J, Bastardot M, Glaizot O, Christe P (2024) Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine bird. bioRxiv ver 3. Peer reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.28.550923 | Spring reproductive success influences autumnal malarial load in a passerine bird | Romain Pigeault, Camille-Sophie Cozzarolo, Jérôme Wassef, Jérémy Gremion, Marc Bastardot, Olivier Glaizot, Philippe Christe | <p>Although avian haemosporidian parasites are widely used as model organisms to study fundamental questions in evolutionary and behavorial ecology of host-parasite interactions, some of their basic characteristics, such as seasonal variations in ... |  | Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Parasites | Claire Loiseau | Carolina Chagas, Anonymous, Luz García-Longoria | 2023-08-11 14:14:56 | View |
29 Jan 2024
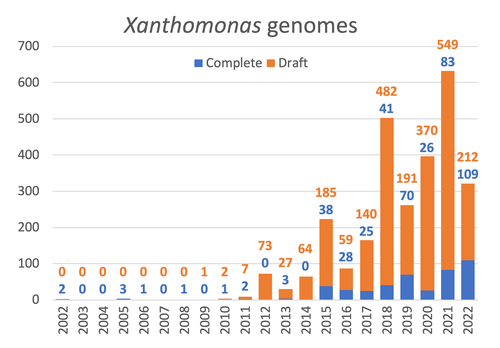
Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the First Xanthomonas Genome Sequences – How Genomics Revolutionized Taxonomy, Provided Insight into the Emergence of Pathogenic Bacteria, Enabled New Fundamental Discoveries and Helped Developing Novel Control Measures – A Perspective from the French Network on XanthomonadsRalf Koebnik, Sophie Cesbron, Nicolas W. G. Chen, Marion Fischer-Le Saux, Mathilde Hutin, Marie-Agnès Jacques, Laurent D. Noël, Alvaro Perez-Quintero, Perrine Portier, Olivier Pruvost, Adrien Rieux, And Boris Szurek https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8223857Advancing Pathogen Genomics: A Comprehensive Review of the Xanthomonas(*) Genome's Impact on Bacterial Research and Control StrategiesRecommended by Damien François Meyer based on reviews by Boris Vinatzer and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Boris Vinatzer and 3 anonymous reviewers
The paper titled "Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the First Xanthomonas Genome Sequences – How Genomics Revolutionized Taxonomy Provided Insight into the Emergence of Pathogenic Bacteria Enabled New Fundamental Discoveries and Helped Developing Novel Control Measures – A Perspective from the French Network on Xanthomonads" by Ralf Koebnik et al. (2023) is an insightful contribution to the field of genomics and its application in understanding pathogenic bacteria, particularly Xanthomonas. This comprehensive review offers a unique perspective from the French Network on Xanthomonads, underscoring the significant advancements in taxonomy, pathogen emergence, and development of control strategies due to genomic research. One of the paper's main strengths is its thorough exploration of how genomics has revolutionized our understanding of Xanthomonas and other pathogenic bacteria. It sheds light on the evolution and emergence of these pathogens, contributing significantly to the development of novel and effective control measures. The authors' detailed account of the historical progress and current state of genomics in this field highlights its pivotal role in guiding future research and practical applications in managing bacterial diseases. Moreover, the paper emphasizes the importance of collaborative efforts and the sharing of knowledge within scientific networks, as exemplified by the French Network on Xanthomonas. This approach not only enriches the study but also serves as a model for future collaborative research endeavors. In conclusion, the work of Koebnik et al. is a valuable resource for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners in the field of plant pathology and genomics. It not only provides a comprehensive overview of the advances in genomics related to Xanthomonas but also illustrates the broader impact of genomic studies in understanding and managing pathogenic bacteria. References Ralf Koebnik, Sophie Cesbron, Nicolas W. G. Chen, Marion Fischer-Le Saux, Mathilde Hutin, Marie-Agnès Jacques, Laurent D. Noël, Alvaro Perez-Quintero, Perrine Portier, Olivier Pruvost, Adrien Rieux, And Boris Szurek (2024) Celebrating the 20th anniversary of the first Xanthomonas genome gequences – How genomics revolutionized taxonomy, provided insight into the emergence of pathogenic bacteria, enabled new fundamental discoveries and helped developing novel control measures – A perspective from the French network on Xanthomonads. Zenodo ver. 3, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8223857 | Celebrating the 20th Anniversary of the First Xanthomonas Genome Sequences – How Genomics Revolutionized Taxonomy, Provided Insight into the Emergence of Pathogenic Bacteria, Enabled New Fundamental Discoveries and Helped Developing Novel Control ... | Ralf Koebnik, Sophie Cesbron, Nicolas W. G. Chen, Marion Fischer-Le Saux, Mathilde Hutin, Marie-Agnès Jacques, Laurent D. Noël, Alvaro Perez-Quintero, Perrine Portier, Olivier Pruvost, Adrien Rieux, And Boris Szurek | <p>In this Opinion paper, members of the French Network on Xanthomonads give their personal view on what they consider to be some of the groundbreaking discoveries in the field of molecular plant pathology over the past 20 years. By celebrating th... |  | Epidemiology, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Molecular biology of infections, Molecular genetics o... | Damien François Meyer | 2023-08-09 10:37:15 | View | |
19 Feb 2024
Population genetics of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the diseaseMoise S. Kagbadouno, Modou Séré, Adeline Ségard, Abdoulaye Dansy Camara, Mamadou Camara, Bruno Bucheton, Jean-Mathieu Bart, Fabrice Courtin, Thierry de Meeûs, Sophie Ravel https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.25.550445Reaching the last miles for transmission interruption of sleeping sickness in Guinea: follow-up of achievements and policy making using microsatellites-based population geneticsRecommended by Hugues Nana Djeunga based on reviews by Fabien HALKETT and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Fabien HALKETT and 2 anonymous reviewers
Thanks to the coordinated and sustained efforts of national control programs, the World Health Organization (WHO), bilateral cooperation and nongovernmental organizations, the incidence of Human African Trypanosomiasis (HAT), better known as sleeping sickness, has drastically decreased during the last two decades (WHO, 2023a). Indeed, between 1999 and 2022, the reported number of new cases of the chronic form of sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense) fell by 97% (from 27 862 to 799), and the number of newly reported cases of the acute form of HAT (Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense) fell by 94% (from 619 to 38) (WHO, 2023b). These encouraging trends led the WHO to target this debilitating and highly fatal (if untreated) vector-borne parasitic disease for elimination as a public health problem by 2020, and for interruption of transmission (zero case) by 2030 (WHO, 2021, WHO, 2023a). However, the disease is persisting in many foci, and even some cases of resurgence have been documented after unfortunate events such as war or pandemics (Moore et al., 1999; Sah et al., 2023. Simarro et al). Although effective control measures, diagnosis and treatment are complex and require specific skills (WHO, 2023), especially in a context which animal reservoirs, including hidden reservoirs, can contribute to the maintenance/persistence of infection (Welburn and Maudlin, 2012; Camara et al., 2021). Vector control therefore appears as a viable alternative to accelerate sleeping sickness transmission interruption, and WHO has identified some critical actions for HAT elimination, including the coordination of vector control and animal trypanosomiasis management among countries, stakeholders and other sectors (e.g. tourism and wildlife) through multisectoral national bodies to maximize synergies (WHO, 2021). The paper by Kagbadouno and Collaborators (2024) uses microsatellite markers genotyping and population genetics tools to investigate the impact of 11 years of tiny target-based vector control on the population biology of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in Boffa, one of the three active sleeping sickness foci in Guinea (Kagbadouno et al., 2012). Although vector control significantly reduced the apparent densities of tsetse flies (and therefore the human exposure to the vector) as well as the prevalence and incidence of the disease in the Boffa HAT focus (Courtin et al., 2015), no genetic signature of vector control was observed as no difference in population size, before and after the onset of the control policy, was found. The authors then provided national programs and implementing partners with indications on the actions to be taken to (i) maintain the achievements of vector control (thus avoiding rebound/resurgence as was experienced in the past (Franco et al., 2014), and (ii) accelerate the momentum towards elimination by for example combining these vector control efforts with medical surveys for case detection and treatment, in line with WHO recommendations (WHO, 2021). References Camara M, Soumah AM, Ilboudo H, Travaillé C, Clucas C, Cooper A, Kuispond Swar NR, Camara O, Sadissou I, Calvo Alvarez E, Crouzols A, Bart JM, Jamonneau V, Camara M, MacLeod A, Bucheton B, Rotureau B. Extravascular Dermal Trypanosomes in Suspected and Confirmed Cases of gambiense Human African Trypanosomiasis. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 1;73(1):12-20. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa897 Courtin F, Camara M, Rayaisse JB, Kagbadouno M, Dama E, Camara O, Traore IS, Rouamba J, Peylhard M, Somda MB, Leno M, Lehane MJ, Torr SJ, Solano P, Jamonneau V, Bucheton B (2015) Reducing human-tsetse contact significantly enhances the efficacy of sleeping sickness active screening campaigns: a promising result in the context of elimination. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003727 Franco JR, Simarro PP, Diarra A, Jannin JG. (2014) Epidemiology of human African trypanosomiasis. Clin Epidemiol. 6:257-75. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S39728 Kagbadouno, M. S., Séré, M., Ségard, A., Camara, A. D., Camara, M., Bucheton, B., ... & Ravel, S. (2023). Population genetics of Glossina palpalis gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the disease. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.25.550445 Kagbadouno MS, Camara M, Rouamba J, Rayaisse JB, Traoré IS, Camara O, Onikoyamou MF, Courtin F, Ravel S, De Meeûs T, Bucheton B, Jamonneau V, Solano P (2012) Epidemiology of sleeping sickness in boffa (Guinea): where are the trypanosomes? PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 6, e1949. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001949 Moore A, Richer M, Enrile M, Losio E, Roberts J, Levy D. Resurgence of sleeping sickness in Tambura County, Sudan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999 Aug;61(2):315-8. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.1999.61.315 Sah R, Mohanty A, Rohilla R, Padhi BK. A resurgence of Sleeping sickness amidst the COVID-19 pandemic: Correspondence. Int J Surg Open. 2023 Apr;53:100604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijso.2023.100604 Welburn SC, Maudlin I. Priorities for the elimination of sleeping sickness. Adv Parasitol. 2012;79:299-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398457-9.00004-4 World Health Organization, 2021. Ending the neglect to attain the Sustainable Development Goals: a road map for neglected tropical diseases 2021–2030. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. ISBN: 978 92 4 001035 2. 196p. World Health Organization, 2023a. Trypanosomiasis, human African (sleeping sickness): key facts. Accessed at https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/trypanosomiasis-human-african-(sleeping-sickness) on February 19, 2023. World Health Organization, 2023b. Human African Trypanosomiasis, (sleeping sickness): the global health observatory. Accessed at https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/human-african-trypanosomiasis on February 19, 2023. | Population genetics of *Glossina palpalis* gambiensis in the sleeping sickness focus of Boffa (Guinea) before and after eight years of vector control: no effect of control despite a significant decrease of human exposure to the disease | Moise S. Kagbadouno, Modou Séré, Adeline Ségard, Abdoulaye Dansy Camara, Mamadou Camara, Bruno Bucheton, Jean-Mathieu Bart, Fabrice Courtin, Thierry de Meeûs, Sophie Ravel | <p style="text-align: justify;">Human African trypanosomosis (HAT), also known as sleeping sickness, is still a major concern in endemic countries. Its cyclical vector are biting insects of the genus Glossina or tsetse flies. In Guinea, the mangro... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors | Hugues Nana Djeunga | 2023-07-29 13:24:52 | View | ||
24 Jan 2024
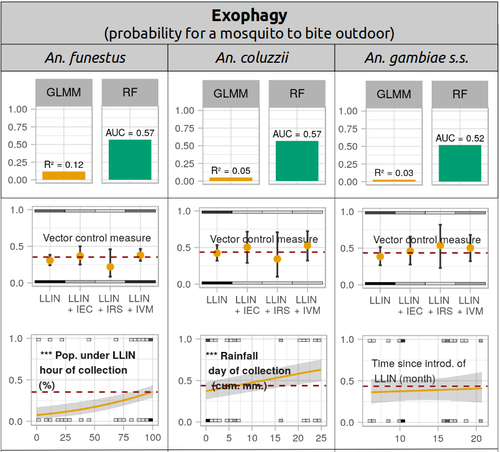
Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictabilityPaul Taconet, Dieudonné Diloma Soma, Barnabas Zogo, Karine Mouline, Frédéric Simard, Alphonsine Amanan Koffi, Roch Kounbobr Dabiré, Cédric Pennetier, Nicolas Moiroux https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.20.504631Large and complete datasets, and modelling reveal the major determinants of physiological and behavioral insecticide resistance of malaria vectorsRecommended by Thierry DE MEEÛS based on reviews by Haoues Alout and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Haoues Alout and 1 anonymous reviewer
Parasites represent the most diverse and adaptable ecological group of the biosphere (Timm & Clauson, 1988; De Meeûs et al., 1998; Poulin & Morand, 2000; De Meeûs & Renaud, 2002). The human species is known to considerably alter biodiversity, though it hosts, and thus sustains the maintenance of a spectacular diversity of parasites (179 species for eukaryotic species only) (De Meeûs et al., 2009). Among these, the five species of malaria agents (genus Plasmodium) remain a major public health issue around the world. Plasmodium falciparum is the most prevalent and lethal of these (Liu et al., 2010). With a pick of up to 2 million deaths due to malaria in 2004, deaths decreased to around 1 million in 2010 (Murray et al., 2012), to reach 619,000 in 2021, most of which in sub-Saharan Africa, and 79% of which were among children aged under 5 years (World Health Organization, 2022). As stressed by Taconet et al. (2023), reduction in malaria deaths is attributable to control measures, in particular against its vectors (mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles). Nevertheless, the success of vector control is hampered by several factors (biological, environmental and socio-economic), and in particular by the great propensity of targeted mosquitoes to evolve physiological or behavioral avoidance of anti-vectorial measures. In their paper Taconet et al. (2023) aims at understanding what are the main factors that determine the evolution of insecticide resistance in several malaria vectors, in relation to the biological determinisms of behavioral resistance and how fast such evolutions take place. To tackle these objectives, authors collected an impressive amount of data in two rural areas of West Africa. With appropriate modeling, Taconet et al. discovered, among many other results, a predominant role of public health measures, as compared to agricultural practices, in the evolution of physiological resistance. They also found that mosquito foraging activities are mostly explained by host availability and climate, with a poor, if any, association with genetic markers of physiological resistance to insecticides. These findings represent an important contribution to the field and should help at designing more efficient control strategies against malaria.
References De Meeûs T, Michalakis Y, Renaud F (1998) Santa Rosalia revisited: or why are there so many kinds of parasites in “the garden of earthly delights”? Parasitology Today, 14, 10–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-4758(97)01163-0 De Meeûs T, Prugnolle F, Agnew P (2009) Asexual reproduction in infectious diseases. In: Lost Sex: The Evolutionary Biology of Parthenogenesis (eds Schön I, Martens K, van Dijk P), pp. 517-533. Springer, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-2770-2_24 De Meeûs T, Renaud F (2002) Parasites within the new phylogeny of eukaryotes. Trends in Parasitology, 18, 247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-4922(02)02269-9 Liu W, Li Y, Learn GH, Rudicell RS, Robertson JD, Keele BF, Ndjango JB, Sanz CM, Morgan DB, Locatelli S, Gonder MK, Kranzusch PJ, Walsh PD, Delaporte E, Mpoudi-Ngole E, Georgiev AV, Muller MN, Shaw GM, Peeters M, Sharp PM, Rayner JC, Hahn BH (2010) Origin of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature, 467, 420–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09442 Murray CJ, Rosenfeld LC, Lim SS, Andrews KG, Foreman KJ, Haring D, Fullman N, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Lopez AD (2012) Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. The Lancet, 379, 413–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60034-8 Poulin R, Morand S (2000) The diversity of parasites. Quarterly Review of Biology, 75, 277–293. https://doi.org/10.1086/393500 Taconet P, Soma DD, Zogo B, Mouline K, Simard F, Koffi AA, Dabire RK, Pennetier C, Moiroux N (2023) Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictability. bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.20.504631 Timm RM, Clauson BL (1988) Coevolution: Mammalia. In: 1988 McGraw-Hill yearbook of science & technology, pp. 212–214. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York. World Health Organization (2022) World malaria report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/365169/9789240064898-eng.pdf?sequence=1.
| Physiological and behavioural resistance of malaria vectors in rural West-Africa : a data mining study to address their fine-scale spatiotemporal heterogeneity, drivers, and predictability | Paul Taconet, Dieudonné Diloma Soma, Barnabas Zogo, Karine Mouline, Frédéric Simard, Alphonsine Amanan Koffi, Roch Kounbobr Dabiré, Cédric Pennetier, Nicolas Moiroux | <p>Insecticide resistance and behavioural adaptation of malaria mosquitoes affect the efficacy of long-lasting insecticide nets - currently the main tool for malaria vector control. To develop and deploy complementary, efficient and cost-effective... |  | Behaviour of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Pesticide resistance, Population genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Vectors | Thierry DE MEEÛS | Haoues Alout, Anonymous | 2023-07-03 11:29:10 | View |
21 Sep 2023
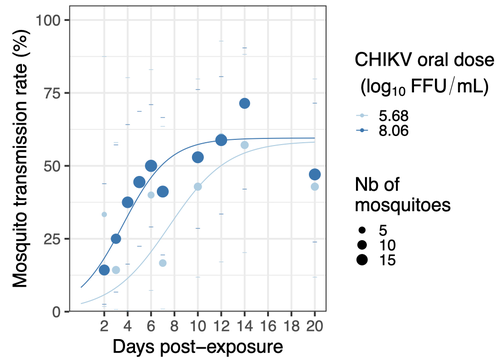
Chikungunya intra-vector dynamics in Aedes albopictus from Lyon (France) upon exposure to a human viremia-like dose range reveals vector barrier permissiveness and supports local epidemic potentialBarbara Viginier, Lucie Cappuccio, Celine Garnier, Edwige Martin, Carine Maisse, Claire Valiente Moro, Guillaume Minard, Albin Fontaine, Sebastian Lequime, Maxime Ratinier, Frederick Arnaud, Vincent Raquin https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.06.22281997Fill in one gap in our understanding of CHIKV intra-vector dynamicsRecommended by Sara Moutailler based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Mosquitoes are first vector of pathogen worldwide and transmit several arbovirus, most of them leading to major outbreaks (1). Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a perfect example of the “explosive type” of arbovirus, as observed in La Réunion Island in 2005-2006 (2-6) and also in the outbreak of 2007 in Italy (7), both vectorized by Ae. albopictus. Being able to better understand CHIKV intra-vector dynamics is still of major interest since not all chikungunya strain are explosive ones (8). In this study (9), the authors have evaluated the vector competence of a local strain of Aedes albopictus (collected in Lyon, France) for CHIKV. They evaluated infection, dissemination and transmission dynamics of CHIKV using different dose of virus in individual mosquitoes from day 2 to day 20 post exposure, by titration and quantification of CHIKV RNA load in the saliva. As highlighted by both reviewers, the most innovative idea in this study was the use of three different oral doses trying to span human viraemia detected in two published studies (10-11), doses that were estimated through their model of human CHIKV viremia in the blood. They have found that CHIKV dissemination from the Ae. albopictus midgut depends on the interaction between time post-exposure and virus dose (already highlighted by other international publications). Then their results were implemented in the agent-based model nosoi to estimate the epidemic potential of CHIKV in a French population of Ae. albopictus, using realistic vectorial capacity parameters. To conclude, the authors have discussed the importance of other parameters that could influence vector competence as mosquito microbiota and temperature, parameters that need also to be estimated in local mosquito population to improve the risk assessment through modelling. As pointed out by both reviewers, this is a nice study, well written and easy to read. These results allow filling in another gap of our understanding of CHIKV intra-vector dynamics and highlight the epidemic potential of CHIKV upon transmission by Aedes albopictus in mainland France. For all these reasons, I chose to recommend this article for Peer Community In Infections. References 1. Marine Viglietta, Rachel Bellone, Adrien Albert Blisnick, Anna-Bella Failloux. (2021). Vector Specificity of Arbovirus Transmission. Front Microbiol Dec 9;12:773211. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.773211 2. Schuffenecker I, Iteman I, Michault A, Murri S, Frangeul L, Vaney M-C, Lavenir R, Pardigon N, Reynes J-M, Pettinelli F, Biscornet L, Diancourt L, Michel S, Duquerroy S, Guigon G, Frenkiel M-P, Bréhin A-C, Cubito N, Desprès P, Kunst F, Rey FA, Zeller H, Brisse S. (2006). Genome Microevolution of Chikungunya viruses Causing the Indian Ocean Outbreak. 2006. PLoS Medicine, 3, e263. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030263 3. Bonilauri P, Bellini R, Calzolari M, Angelini R, Venturi L, Fallacara F, Cordioli P, 687 Angelini P, Venturelli C, Merialdi G, Dottori M. (2008). Chikungunya Virus in Aedes albopictus, Italy. Emerging Infectious 689 Diseases, 14, 852–854. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1405.071144 4. Pagès F, Peyrefitte CN, Mve MT, Jarjaval F, Brisse S, Iteman I, Gravier P, Tolou H, Nkoghe D, Grandadam M. (2009). Aedes albopictus Mosquito: The Main Vector of the 2007 Chikungunya Outbreak in Gabon. PLoS ONE, 4, e4691. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004691 5. Paupy C, Kassa FK, Caron M, Nkoghé D, Leroy EM (2012) A Chikungunya Outbreak Associated with the Vector Aedes albopictus in Remote Villages of Gabon. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 12, 167–169. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0736 6. Mombouli J-V, Bitsindou P, Elion DOA, Grolla A, Feldmann H, Niama FR, Parra H-J, Munster VJ. (2013). Chikungunya Virus Infection, Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2011. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 19, 1542–1543. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1909.130451 7. Venturi G, Luca MD, Fortuna C, Remoli ME, Riccardo F, Severini F, Toma L, Manso MD, Benedetti E, Caporali MG, Amendola A, Fiorentini C, Liberato CD, Giammattei R, Romi R, Pezzotti P, Rezza G, Rizzo C. (2017). Detection of a chikungunya outbreak in Central Italy, August to September 2017. Eurosurveillance, 22, 17–00646. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.es.2017.22.39.17-00646 8. de Lima Cavalcanti, T.Y.V.; Pereira, M.R.; de Paula, S.O.; Franca, R.F.d.O. (2022). A Review on Chikungunya Virus Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Current Vaccine Development. Viruses 2022, 14, 969. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050969 9. Barbara Viginier, Lucie Cappuccio, Celine Garnier, Edwige Martin, Carine Maisse, Claire Valiente Moro, Guillaume Minard, Albin Fontaine, Sebastian Lequime, Maxime Ratinier, Frederick Arnaud, Vincent Raquin. (2023). Chikungunya intra-vector dynamics in Aedes albopictus from Lyon (France) upon exposure to a human viremia-like dose range reveals vector barrier permissiveness and supports local epidemic potential. medRxiv, ver.3, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.06.22281997 10. Appassakij H, Khuntikij P, Kemapunmanus M, Wutthanarungsan R, Silpapojakul K (2013) Viremic profiles in CHIKV-infected cases. Transfusion, 53, 2567–2574. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03960.x 11. Riswari SF, Ma’roef CN, Djauhari H, Kosasih H, Perkasa A, Yudhaputri FA, Artika IM, Williams M, Ven A van der, Myint KS, Alisjahbana B, Ledermann JP, Powers AM, Jaya UA (2015) Study of viremic profile in febrile specimens of chikungunya in Bandung, Indonesia. Journal of clinical virology : the official publication of the Pan American Society for Clinical Virology, 74, 61–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2015.11.017 | Chikungunya intra-vector dynamics in *Aedes albopictus* from Lyon (France) upon exposure to a human viremia-like dose range reveals vector barrier permissiveness and supports local epidemic potential | Barbara Viginier, Lucie Cappuccio, Celine Garnier, Edwige Martin, Carine Maisse, Claire Valiente Moro, Guillaume Minard, Albin Fontaine, Sebastian Lequime, Maxime Ratinier, Frederick Arnaud, Vincent Raquin | <p>Arbovirus emergence and epidemic potential, as approximated by the vectorial capacity formula, depends on host and vector parameters, including the vector intrinsic ability to replicate then transmit the pathogen known as vector competence. Vec... |  | Epidemiology, Vectors, Viruses | Sara Moutailler | 2023-06-17 15:59:17 | View | |
28 May 2024
HIV self-testing positivity rate and linkage to confirmatory testing and care: a telephone survey in Côte d'Ivoire, Mali and SenegalKra Djuhe Arsene Kouassi, Arlette Simo Fotso, Nicolas Rouveau, Mathieu Maheu-Giroux, Marie-Claude Boily, Romain Silhol, Marc d'Elbee, Anthony Vautier, Joseph Larmarange, ATLAS Team https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.10.23291206The benefits of HIV self-testing in West Africa: quantified.Recommended by Jessie Abbate based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersDespite decades of advances and understanding of the indiscriminate nature of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), it remains shrouded in stigma that makes it difficult to reach some key populations at risk of transmission. The advent of self-testing technology for HIV (HIVST) has opened much-needed potential for bringing privacy to prevention that is crucial for curtailing its continued spread (Johnson et al., 2014). The HIV Self-Testing in Africa (STAR) Initiative (https://www.psi.org/fr/project/star/), carried out in Eastern and Southern Africa between 2015 and 2020 (Simwinga et al., 2022), demonstrated the market and public health operational potential of HIVST of different distribution methods. From 2019 to 2022, the “AutoTest de dépistage du VIH : Libre d’Accéder à la connaissance de son Statut" (ATLAS, translating to “HIVST: Freedom to know your status”) program built on these findings to quantify the public health value of HIVST for reaching key populations in West Africa (specifically, Mali, Senegal and Côte d’Ivoire) (Ky-Zerbo et al., 2022). The innovative secondary distribution methods these studies employed, where the primary targeted populations were also encouraged to take and provide tests to their contacts, helped widen the reach of HIVST within key population networks beyond those relying on access to HIV testing facilities.
The tricky part of the self-testing model lies in assessing its reach and impact while maintaining the privacy of self-testers that is central to its success. Following voluntary phone survey methods that previously were able to show expanded reach of HIVST to first-time testers in key populations in West Africa and high rates of confirmatory testing and treatment seeking (Kra et al., 2022), Kra et al. (Kra et al., 2024) quantified how many of these self-tests led to a positive result – allowing wider assessment of follow-up behaviors and positivity rates among the hard-to-reach populations the program had targeted.
While the numbers were low, the results were informative. Among respondents who reported a positive (“reactive”) HIVST, just 44% proceeded to confirmatory testing. This is lower than in other populations where HIVST follow-up has been assessed (Thirumurthy et al., 2016). The main reasons given for not confirming a reactive self-test was misinterpretation of HIVST results and not understanding that confirmatory testing was needed. The result thus highlighted a need for improved communication on how to correctly interpret HIVST results, and the authors provided ranges for how this misinterpretation could have affected their positivity estimates. However, the majority of those who sought confirmatory testing did so within 3 months, and nearly all of those with confirmed infection started on treatment. HIV positivity rates in the three countries were all higher than other published HIV positivity estimates (Giguère et al., 2021; Maheu-Giroux et al., 2019), suggesting that HIVST methods were highly effective at reaching the targeted communities. Finally, while the authors demonstrated their methods as an effective way of assessing the utility of HIVST campaigns and identifying ways to improve them, the follow-up surveys are likely too costly to replace current passive surveillance methods for assessing community disease burden. That said, these precious data should be taken as validation of the public health value of HIV self-testing in key populations across communities in West Africa. With improvements in communicating instructions for use and follow-up, there is little doubt that the innovation of HIVST primary and secondary distribution could become a widely useful addition to the fight against HIV.
References Giguère, K., Eaton, J. W., Marsh, K., Johnson, L. F., Johnson, C. C., Ehui, E., Jahn, A., Wanyeki, I., Mbofana, F., Bakiono, F., Mahy, M., & Maheu-Giroux, M. (2021). Trends in knowledge of HIV status and efficiency of HIV testing services in sub-Saharan Africa, 2000–20: a modelling study using survey and HIV testing programme data. The Lancet HIV, 8(5), e284–e293. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30315-5 Johnson, C., Baggaley, R., Forsythe, S., Van Rooyen, H., Ford, N., Napierala Mavedzenge, S., Corbett, E., Natarajan, P., & Taegtmeyer, M. (2014). Realizing the potential for HIV self-testing. In AIDS and Behavior (Vol. 18, Issue SUPPL. 4). Springer New York LLC. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-014-0832-x Kra, A. K., Fosto, A. S., N’guessan, K. N., Geoffroy, O., Younoussa, S., Kabemba, O. K., Gueye, P. A., Ndeye, P. D., Rouveau, N., Boily, M. C., Silhol, R., d’Elbée, M., Maheu-Giroux, M., Vautier, A., & Larmarange, J. (2022). Can HIV self-testing reach first-time testers? A telephone survey among self-test end users in Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, and Senegal. BMC Infectious Diseases, 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-023-08626-w Kra, A. K., Fotso, A. S., Rouveau, N., Maheu-Giroux, M., Boily, M.-C., Silhol, R., d’Elbée, M., Vautier, A., Lamarange, J., & the Atlas team. (2024). HIV self-testing positivity rate and linkage to confirmatory testing and care: a telephone survey in Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, and Senegal. MedRxiv, Ver. 4 Peer-Reviewed and Recommended by Peer Community in Infections, 2023.06.10.23291206. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.10.23291206 Ky-Zerbo, O., Desclaux, A., Boye, S., Maheu-Giroux, M., Rouveau, N., Vautier, A., Camara, C. S., Kouadio, B. A., Sow, S., Doumenc-Aidara, C., Gueye, P. A., Geoffroy, O., Kamemba, O. K., Ehui, E., Ndour, C. T., Keita, A., & Larmarange, J. (2022). “I take it and give it to my partners who will give it to their partners”: Secondary distribution of HIV self-tests by key populations in Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, and Senegal. BMC Infectious Diseases, 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-023-08319-4 Maheu-Giroux, M., Marsh, K., Doyle, C. M., Godin, A., Lanièce Delaunay, C., Johnson, L. F., Jahn, A., Abo, K., Mbofana, F., Boily, M. C., Buckeridge, D. L., Hankins, C. A., & Eaton, J. W. (2019). National HIV testing and diagnosis coverage in sub-Saharan Africa: A new modeling tool for estimating the “first 90” from program and survey data. AIDS, 33, S255–S269. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000002386 Simwinga, M., Gwanu, L., Hensen, B., Sigande, L., Mainga, M., Phiri, T., Mwanza, E., Kabumbu, M., Mulubwa, C., Mwenge, L., Bwalya, C., Kumwenda, M., Mubanga, E., Mee, P., Johnson, C. C., Corbett, E. L., Hatzold, K., Neuman, M., Ayles, H., & Taegtmeyer, M. (2022). Lessons learned from implementation of four HIV self-testing (HIVST) distribution models in Zambia: applying the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to understand impact of contextual factors on implementation. BMC Infectious Diseases, 22(Suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-024-09168-5 Thirumurthy, H., Masters, S. H., Mavedzenge, S. N., Maman, S., Omanga, E., & Agot, K. (2016). Promoting male partner HIV testing and safer sexual decision making through secondary distribution of self-tests by HIV-negative female sex workers and women receiving antenatal and post-partum care in Kenya: a cohort study. The Lancet HIV, 3(6), e266–e274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(16)00041-2
| HIV self-testing positivity rate and linkage to confirmatory testing and care: a telephone survey in Côte d'Ivoire, Mali and Senegal | Kra Djuhe Arsene Kouassi, Arlette Simo Fotso, Nicolas Rouveau, Mathieu Maheu-Giroux, Marie-Claude Boily, Romain Silhol, Marc d'Elbee, Anthony Vautier, Joseph Larmarange, ATLAS Team | <p>HIV self-testing (HIVST) empowers individuals to decide when and where to test and with whom to share their results. From 2019 to 2022, the ATLAS program distributed ~ 400 000 HIVST kits in Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, and Senegal. It prioritised key p... |  | Epidemiology | Jessie Abbate | 2023-06-16 16:40:51 | View | |
17 Jan 2024
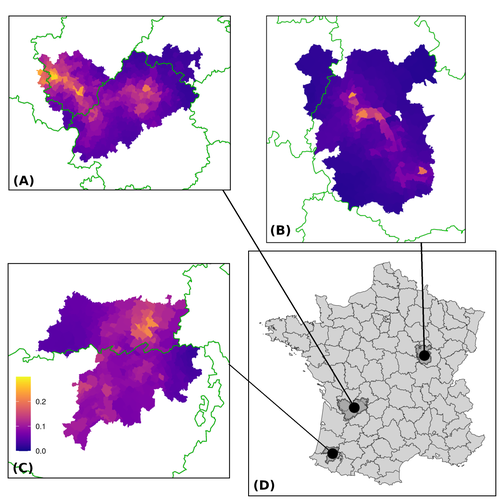
Assessing the dynamics of Mycobacterium bovis infection in three French badger populationsClement CALENGE, Ariane PAYNE, Edouard REVEILLAUD, Celine RICHOMME, Sebastien GIRARD, Stephanie DESVAUX https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.31.543041From disease surveillance to public action. Re-inforcing both epidemiological surveillance and data analysis: an illustration with Mycobacterium bovisRecommended by Jean-Francois Guégan based on reviews by Rowland Kao and 1 anonymous reviewerMycobacterium bovis, also called M. tuberculosis var. bovis, is a bacterium belonging to the M. tuberculosis complex (i.e., MTBC) and which can cause through zoonotic transmission another form of human tuberculosis (Tb). It is above all the agent of bovine tuberculosis (i.e., bTb) which affects not only cattle (wild or farmed) but also a large diversity of other wild mammals worldwide. An increasing number of infected animal cases are being discovered in many regions of the world, thus raising the problem of tuberculosis transmission, including to humans, more complex than previously thought. Efforts have been made in terms of vaccination or culling of populations of host carrier species, such as the badger for example, however leading to consequences of greater dispersion of the infectious agent. M. bovis shows a more or less significant capacity to persist outside its hosts, particularly in the environment under certain abiotic and biotic conditions. This bacillus can be transmitted and spread in many ways, including through aerosol, mucus and sputum, urine and feces, by direct contact with infected animals, their dead bodies or rather via their excreta or by inhalation of aerosols, depending on the host species concerned. In this paper, Calenge and his collaborators (Callenge et al. 2024) benefited from a national surveillance program on M. bovis cases in wild species, set up in 2011 in France, i.e., Sylvatub, for detecting and monitoring M. bovis infection in European badger (Meles meles) populations. Sylvatub is a participatory program involving both national and local stakeholder systems in order to determine changes in bTb infection levels in domestic and wild animal species. This original work had two aims: to describe spatial disease dynamics in the three clusters under scrutiny using a complex Bayesian model; and to develop indicators for the monitoring of the M. bovis infection by stakeholders and decision-makers of the program. This paper is timely and very comprehensive. In this cogent study, the authors illustrate this point by using epidemiological surveillance to obtain large amounts of data (which is generally lacking in human epidemiology, but more dramatically lacking in animal epidemiology) and a highly sophisticated biostatistical analysis (Callenge et al. 2024). It is in itself a demonstration of the current capabilities of population dynamics applied to infectious disease situations, in this case animal, in the rapidly developing discipline of disease ecology and evolution. One of the aims of the study is to propose statistical models that can be used by the different stakeholders in charge, for instance, of wildlife conservation or the regional or State veterinary services to assess disease risk in the most affected regions. References Assel AKHMETOVA, Jimena GUERRERO, Paul McADAM, Liliana CM SALVADOR, Joseph CRISPELL, John LAVERY, Eleanor PRESHO, Rowland R KAO, Roman BIEK, Fraser MENZIES, Nigel TRIMBLE, Roland HARWOOD, P Theo PEPLER, Katarina ORAVCOVA, Jordon GRAHAM, Robin SKUCE, Louis DU PLESSIS, Suzan THOMPSON, Lorraine WRIGHT, Andrew W BYRNE, Adrian R ALLEN. 2023. Genomic epidemiology of Mycobacterium bovis infection in sympatric badger and cattle populations in Northern Ireland. Microbial Genomics 9: mgen001023. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.001023 Roman BIEK, Anthony O’HARE, David WRIGHT, Tom MALLON, Carl McCORMICK, Richard J ORTON, Stanley McDOWELL, Hannah TREWBY, Robin A SKUCE, Rowland R KAO. 2012. Whole genome sequencing reveals local transmission patterns of Mycobacterium bovis in sympatric cattle and badger populations. PLoS Pathogens 8: e1003008. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003008 Clément CALENGE, Ariane PAYNE, Edouard REVEILLAUD, Céline RICHOMME, Sébastien GIRARD, Stephanie DESVAUX. 2024. Assessing the dynamics of Mycobacterium bovis infection in three French badger populations. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.31.543041 Marc CHOISY, Pejman ROHANI. 2006. Harvesting can increase severity of wildlife disease epidemics. Proceedings of the Royal Society, London, Ser. B 273: 2025-2034. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2006.3554 Shannon C DUFFY, Sreenidhi SRINIVASAN, Megan A SCHILLING, Tod STUBER, Sarah N DANCHUK, Joy S MICHAEL, Manigandan VENKATESAN, Nitish BANSAL, Sushila MAAN, Naresh JINDAL, Deepika CHAUDHARY, Premanshu DANDAPAT, Robab KATANI, Shubhada CHOTHE, Maroudam VEERASAMI, Suelee ROBBE-AUSTERMAN, Nicholas JULEFF, Vivek KAPUR, Marcel A BEHR. 2020. Reconsidering Mycobacterium bovis as a proxy for zoonotic tuberculosis: a molecular epidemiological surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 1: e66-e73. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30038-0 Jean-François GUEGAN. 2019. The nature of ecology of infectious disease. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 19. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1473-3099(19)30529-8 Brandon H HAYES, Timothée VERGNE, Mathieu ANDRAUD, Nicolas ROSE. 2023. Mathematical modeling at the livestock-wildlife interface: scoping review of drivers of disease transmission between species. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 10: 1225446. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2023.1225446 David KING, Tim ROPER, Douglas YOUNG, Mark EJ WOOLHOUSE, Dan COLLINS, Paul WOOD. 2007. Bovine tuberculosis in cattle and badgers. Report to Secretary of State about tuberculosis in cattle and badgers. London, UK. https://www.bovinetb.info/docs/RBCT_david_%20king_report.pdf Robert MM SMITH , Francis DROBNIEWSKI, Andrea GIBSON, John DE MONTAGUE, Margaret N LOGAN, David HUNT, Glyn HEWINSON, Roland L SALMON, Brian O’NEILL. 2004. Mycobacterium bovis Infection, United Kingdom. Emerging Infectious Diseases 10: 539-541. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1003.020819 | Assessing the dynamics of *Mycobacterium bovis* infection in three French badger populations | Clement CALENGE, Ariane PAYNE, Edouard REVEILLAUD, Celine RICHOMME, Sebastien GIRARD, Stephanie DESVAUX | <p>The Sylvatub system is a national surveillance program established in 2011 in France to monitor infections caused by <em>Mycobacterium bovis</em>, the main etiologic agent of bovine tuberculosis, in wild species. This participatory program, inv... |  | Animal diseases, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Epidemiology, Geography of infectious diseases, Pathogenic/Symbiotic Bacteria, Zoonoses | Jean-Francois Guégan | 2023-06-05 10:50:49 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Jorge Amich
Christine Chevillon
Fabrice Courtin
Christine Coustau
Thierry De Meeûs
Heather R. Jordan
Karl-Heinz Kogel
Yannick Moret
Thomas Pollet
Benjamin Roche
Benjamin Rosenthal
Bashir Salim
Lucy Weinert










