Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
21 Jul 2022

Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV)Nurul Novelia Fuandila, Anne-Sophie Gosselin-Grenet, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sven M Bergmann, Jean-Michel Escoubas, Sandro Klafack, Angela Mariana Lusiastuti, Munti Yuhana, Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier, Jean-Christophe Avarre, Emira Cherif https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.483410Understanding the in vitro evolution of Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3), a story of structural variations that can lead to the design of attenuated virus vaccinesRecommended by Jorge Amich based on reviews by Lucie Cappuccio and Veronique Hourdel based on reviews by Lucie Cappuccio and Veronique Hourdel
Structural variations (SVs) play a key role in viral evolution, and therefore they are also important for infection dynamics. However, the contribution of structural variations to the evolution of double-stranded viruses is limited. This knowledge can help to understand the population dynamics and might be crucial for the future development of viral attenuated vaccines. In this study, Fuandila et al (1) use the Cyprinid herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3), commonly known as koi herpesvirus (KHV), to investigate the variability and contribution of structural variations (SV) for viral evolution after 99 passages in vitro. This virus, with the largest genome among herperviruses, causes a lethal infection in common carp and koi associated with mortalities up to 95% (2). Interestingly, KHV infections are caused by haplotype mixtures, which possibly are a source of genome diversification, but make genomic comparisons more difficult. The authors have used ultra-deep long-read sequencing of two passages, P78 and P99, which were previously described to have differences in virulence. They have found a surprisingly high and wide distribution of SVs along the genome, which were enriched in inversion and deletion events and that often led to defective viral genomes. Although it is known that these defective viral genomes negatively impact viral replication, their implications for virus persistence are still unclear. Subsequently, the authors concentrated on the virulence-relevant region ORF150, which was found to be different in P78 (deletion in 100% of the reads) and P99 (reference-like haplotype). To understand this loss and gain of full ORF150, they searched for SV turn-over in 10 intermediate passages. This analysis revealed that by passage 10 deleted and inverted (attenuated) haplotypes had already appeared, steadily increased frequency until P78, and then completely disappeared between P78 and P99. This is a striking result that raises new questions as to how this clearance occurs, which is really important as these reversions may result in undesirable increases in virulence of live-attenuated vaccines. We recommend this preprint because its use of ultra-deep long-read sequencing has permitted to better understand the role of SV diversity and dynamics in viral evolution. This study shows an unexpectedly high number of structural variations, revealing a novel source of virus diversification and confirming the different mixtures of haplotypes in different passages, including the gain of function. This research provides basic knowledge for the future design of live-attenuated vaccines, to prevent the reversion to virulent viruses. References (1) Fuandila NN, Gosselin-Grenet A-S, Tilak M-K, Bergmann SM, Escoubas J-M, Klafack S, Lusiastuti AM, Yuhana M, Fiston-Lavier A-S, Avarre J-C, Cherif E (2022) Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV). bioRxiv, 2022.03.10.483410, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.10.483410 (2) Sunarto A, McColl KA, Crane MStJ, Sumiati T, Hyatt AD, Barnes AC, Walker PJ. Isolation and characterization of koi herpesvirus (KHV) from Indonesia: identification of a new genetic lineage. Journal of Fish Diseases, 34, 87-101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2010.01216.x | Structural variation turnovers and defective genomes: key drivers for the in vitro evolution of the large double-stranded DNA koi herpesvirus (KHV) | Nurul Novelia Fuandila, Anne-Sophie Gosselin-Grenet, Marie-Ka Tilak, Sven M Bergmann, Jean-Michel Escoubas, Sandro Klafack, Angela Mariana Lusiastuti, Munti Yuhana, Anna-Sophie Fiston-Lavier, Jean-Christophe Avarre, Emira Cherif | <p style="text-align: justify;">Structural variations (SVs) constitute a significant source of genetic variability in virus genomes. Yet knowledge about SV variability and contribution to the evolutionary process in large double-stranded (ds)DNA v... |  | Animal diseases, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Viruses | Jorge Amich | Lucie Cappuccio, Veronique Hourdel | 2022-03-11 10:50:50 | View |
25 Apr 2023

The distribution, phenology, host range and pathogen prevalence of Ixodes ricinus in France: a systematic map and narrative reviewGrégoire Perez, Laure Bournez, Nathalie Boulanger, Johanna Fite, Barbara Livoreil, Karen D. McCoy, Elsa Quillery, Magalie René-Martellet, and Sarah I. Bonnet https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537315An extensive review of Ixodes ricinus in European FranceRecommended by Ana Sofia Santos based on reviews by Ana Palomar and 1 anonymous reviewerTicks are obligate, bloodsucking, nonpermanent ectoparasitic arthropods. Among them, Ixodes ricinus is a classic example of an extreme generalist tick, presenting a highly permissive feeding behavior using different groups of vertebrates as hosts, such as mammalian (including humans), avian and reptilian species (Hoogstraal & Aeschlimann, 1982; Dantas-Torresa & Otranto, 2013). This ecological adaptation can account for the broad geographical distribution of I. ricinus populations, which extends from the western end of the European continent to the Ural Mountains in Russia, and from northern Norway to the Mediterranean basin, including the North African countries - Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia (https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/disease-vectors/surveillance-and-disease-data/tick-maps). The contact with different hosts also promotes the exposure/acquisition and transmission of various pathogenic agents (viruses, bacteriae, protists and nematodes) of veterinary and medical relevance (Aeschlimann et al., 1979). As one of the prime ticks found on humans, this species is implicated in diseases such as Lyme borreliosis, Spotted Fever Group rickettsiosis, Human Anaplasmosis, Human Babesiosis and Tick-borne Encephalitis (Velez et al., 2023). The climate change projections drawn for I. ricinus, in the scenario of global warming, point for the expansion/increase activity in both latitude and altitude (Medlock et al., 2013). The adequacy of vector modeling is relaying in the proper characterization of complex biological systems. Thus, it is essential to increase knowledge on I. ricinus, focusing on aspects such as genetic background, ecology and eco-epidemiology on a microscale but also at a country and region level, due to possible local adaptations of tick populations and genetic drift. In the present systematic revision, Perez et al. (2023) combine old and recently published data (mostly up to 2020) regarding I. ricinus distribution, phenology, host range and pathogen association in continental France and Corsica Island. Based on a keyword search of peer-reviewed papers on seven databases, as well as other sources of grey literature (mostly, thesis), the authors have synthesized information on: 1) Host parasitism to detect potential differences in host use comparing to other areas in Europe; 2) The spatiotemporal distribution of I. ricinus, to identify possible geographic trends in tick density, variation in activity patterns and the influence of environmental factors; 3) Tick-borne pathogens detected in this species, to better assess their spatial distribution and variation in exposure risk. As pointed out by both reviewers, this work clearly summarizes the information regarding I. ricinus and associated microorganisms from European France. This review also identifies remaining knowledge gaps, providing a comparable basis to orient future research. This is why I chose to recommend Perez et al (2023)'s preprint for Peer Community Infections. REFERENCES Aeschlimann, A., Burgdorfer, W., Matile, H., Peter, O., Wyler, R. (1979) Aspects nouveaux du rôle de vecteur joué par Ixodes ricinus L. en Suisse. Acta Tropica, 36, 181-191. Dantas-Torresa, F., Otranto, D. (2013) Seasonal dynamics of Ixodes ricinus on ground level and higher vegetation in a preserved wooded area in southern Europe. Veterinary Parasitology, 192, 253- 258. Hoogstraal, H., Aeschlimann, A. (1982) Tick-host specificity. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 55, 5-32. Medlock, J.M., Hansford, K.M., Bormane, A., Derdakova, M., Estrada-Peña, A., George, J.C., Golovljova, I., Jaenson, T.G.T., Jensen, J.K., Jensen, P.M., Kazimirova, M., Oteo, J.A., Papa, A., Pfister, K., Plantard, O., Randolph, S.E., Rizzoli, A., Santos-Silva, M.M., Sprong, H., Vial, L., Hendrickx, G., Zeller, H., Van Bortel, W. (2013) Driving forces for changes in geographical distribution of Ixodes ricinus ticks in Europe. Parasites and Vectors, 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-6-1 Perez, G., Bournez, L., Boulanger, N., Fite, J., Livoreil, B., McCoy, K., Quillery, E., René-Martellet, M., Bonnet, S. (2023) The distribution, phenology, host range and pathogen prevalence of Ixodes ricinus in France: a systematic map and narrative review. bioRxiv, ver. 1 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.18.537315 Velez, R., De Meeûs, T., Beati, L., Younsi, H., Zhioua, E., Antunes, S., Domingos, A., Ataíde Sampaio, D., Carpinteiro, D., Moerbeck, L., Estrada-Peña, A., Santos-Silva, M.M., Santos, A.S. (2023) Development and testing of microsatellite loci for the study of population genetics of Ixodes ricinus Linnaeus, 1758 and Ixodes inopinatus Estrada-Peña, Nava & Petney, 2014 (Acari: Ixodidae) in the western Mediterranean region. Acarologia, 63, 356-372. https://doi.org/10.24349/bvem-4h49 | The distribution, phenology, host range and pathogen prevalence of *Ixodes ricinus* in France: a systematic map and narrative review | Grégoire Perez, Laure Bournez, Nathalie Boulanger, Johanna Fite, Barbara Livoreil, Karen D. McCoy, Elsa Quillery, Magalie René-Martellet, and Sarah I. Bonnet | <p style="text-align: justify;">The tick <em>Ixodes ricinus</em> is the most important vector species of infectious diseases in European France. Understanding its distribution, phenology, and host species use, along with the distribution and preva... |  | Animal diseases, Behaviour of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Epidemiology, Geography of infectious diseases, Interactions between hosts and infectious ag... | Ana Sofia Santos | 2022-12-06 14:52:44 | View | |
23 Mar 2023
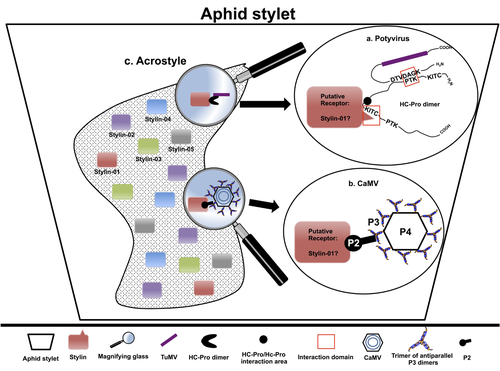
The helper strategy in vector-transmission of plant virusesDi Mattia Jérémy, Zeddam Jean Louis, Uzest Marilyne and Stéphane Blanc https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7709290The intriguing success of helper components in vector-transmission of plant viruses.Recommended by Christine Coustau based on reviews by Jamie Bojko and Olivier SchumppMost plant-infecting viruses rely on an animal vector to be transmitted from one sessile host plant to another. A fascinating aspect of virus-vector interactions is the fact that viruses from different clades produce different proteins to bind vector receptors (1). Two major processes are described. In the “capsid strategy”, a motif of the capsid protein is directly binding to the vector receptor. In the “helper strategy”, a non-structural component, the helper component (HC), establishes a bridge between the virus particle and the vector’s receptor. In this exhaustive review focusing on hemipteran insect vectors, Di Mattia et al. (2) are revisiting the helper strategy in light of recent results. The authors first place the discoveries of the HC strategy in a historical context, suggesting that HC are exclusively found in non-circulative viruses (viruses that only attach to the vector). They present an overview of the nature and modes of action of helper components in the major virus clades of non-circulative viruses (Potyviruses and Caulimoviruses). Authors then detail recent advances, to which they have significantly contributed, showing that the helper strategy also appears widespread in circulative transmission categories (Tenuiviruses, Nanoviruses). In an extensive perspective section, they raise the question of the evolutionary significance of the existence of HC in numerous unrelated viruses, transmitted by unrelated vectors through different mechanisms. They explore the hypothesis that the helper strategy evolved several times independently in distinct viral clades and for different reasons. In particular, they present several potential benefits of plant virus HC related to virus cooperation, collective transmission and effector-driven infectivity. As pointed out by both reviewers, this is a very clear and synthetic review. Di Mattia et al. present an exhaustive overview of virus HC-vector molecular interactions and address functionally and evolutionarily important questions. This review should benefit a large audience interested in host-virus interactions and transmission processes. REFERENCES (1) Ng JCK, Falk BW (2006) Virus-Vector Interactions Mediating Nonpersistent and Semipersistent Transmission of Plant Viruses. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 44, 183–212. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143325 (2) Di Mattia J, Zeddam J-L, Uzest M, Blanc S (2023) The helper strategy in vector-transmission of plant viruses. Zenodo, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7709290 | The helper strategy in vector-transmission of plant viruses | Di Mattia Jérémy, Zeddam Jean Louis, Uzest Marilyne and Stéphane Blanc | <p>An intriguing aspect of vector-transmission of plant viruses is the frequent involvement of a helper component (HC). HCs are virus-encoded non-structural proteins produced in infected plant cells that are mandatory for the transmission success.... |  | Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Molecular biology of infections, Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Plant diseases, Vectors, Viruses | Christine Coustau | 2022-10-28 17:32:39 | View | |
07 Feb 2023
Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populationsMarie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084Unveiling the complex interactions between members of gut microbiomes: a significant advance provided by an exhaustive study of wild bank volesRecommended by Thomas Pollet based on reviews by Jason Anders and 1 anonymous reviewerThe gut of vertebrates is a host for hundreds or thousands of different species of microorganisms named the gut microbiome. This latter may differ greatly in natural environments between individuals, populations and species (1). The vertebrate gut microbiome plays key roles in host fitness through functions including nutrient acquisition, immunity and defense against infectious agents. While bank voles are small mammals potentially reservoirs of a large number of infectious agents, questions about the links between their gut microbiome and the presence of pathogens are scarcely addressed. In this study, Bouilloud et al. (2) used complementary analyses of community and microbial ecology to (i) assess the variability of gut bacteriome diversity and composition in wild populations of the bank vole Myodes glareolus collected in four different sites in Eastern France and (ii) evaluate the three-way interactions between the gut bacteriota, the gastro-intestinal helminths and pathogenic bacteria detected in the spleen. Authors identified important variations of the gut bacteriota composition and diversity among bank voles mainly explained by sampling localities. They found positive correlations between the specific richness of both the gut bacteria and the helminth community, as well as between the composition of these two communities, even when accounting for the influence of geographical distance. The helminths Aonchotheca murissylvatici, Heligmosomum mixtum and the bacteria Bartonella sp were the main taxa associated with the whole gut bacteria composition. Besides, changes in relative abundance of particular gut bacterial taxa were specifically associated with other helminths (Mastophorus muris, Catenotaenia henttoneni, Paranoplocephala omphalodes and Trichuris arvicolae) or pathogenic bacteria. Infections with Neoehrlichia mikurensis, Orientia sp, Rickettsia sp and P. omphalodes were especially associated with lower relative abundance of members of the family Erysipelotrichaceae (Firmicutes), while coinfections with higher number of bacterial infections were associated with lower relative abundance of members of the Bacteroidales family (Bacteroidetes). As pointed out by both reviewers, this study represents a significant advance in the field. I would like to commend the authors for this enormous work. The amount of data, analyses and results is considerable which has sometimes complicated the understanding of the story at the beginning of the evaluation process. Thanks to constructive scientific interactions with both reviewers through the two rounds of evaluation, the authors have efficiently addressed the reviewer's concerns and improved the manuscript, making this great story easier to read. The innovative results of this study emphasize the complex interlinkages between gut bacteriome and infections in wild animal populations and I strongly recommend this article for publication In Peer Community Infections. References (1) Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Sklar J, Jiang L, Natarajan L, Knight R, Belkaid Y (2020) Host variables confound gut microbiota studies of human disease. Nature, 587, 448–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2881-9 (2) Bouilloud M, Galan M, Dubois A, Diagne C, Marianneau P, Roche B, Charbonnel N (2023) Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations. biorxiv, 2022.05.23.493084, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.23.493084 | Three-way relationships between gut microbiota, helminth assemblages and bacterial infections in wild rodent populations | Marie Bouilloud, Maxime Galan, Adelaide Dubois, Christophe Diagne, Philippe Marianneau, Benjamin Roche, Nathalie Charbonnel | <p>Background</p> <p>Despite its central role in host fitness, the gut microbiota may differ greatly between individuals. This variability is often mediated by environmental or host factors such as diet, genetics, and infections. Recently, a part... | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Interactions between hosts and infectious agents/vectors, Reservoirs, Zoonoses | Thomas Pollet | 2022-05-25 10:13:23 | View | ||
14 Dec 2022

Transcriptome responses of the aphid vector Myzus persicae are shaped by identities of the host plant and the virusQuentin Chesnais, Victor Golyaev, Amandine Velt, Camille Rustenholz, Maxime Verdier, Véronique Brault, Mikhail M. Pooggin, Martin Drucker https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500449How do multiple host plants and virus species challenge aphid molecular machinery?Recommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Juan José Lopez Moya and Michelle HeckThe impact of virus infection of a plant on an aphid’s behaviour has been observed in many studies [1]. Indeed, virus infection can alter plant biochemistry through the emission of volatile organic compounds and plant tissue content modification. These alterations can further impact the interactions between plants and aphids. However, although it is a well-known phenomenon, very few studies have explored the consequences of plant virus infection on the gene expression of aphids to understand better the aphid’s manipulation by the plant virus. In this context, the recommended study [2] reports a comprehensive transcriptomic analysis of the genes expressed by one aphid species, Myzus persicae, a vector of several plant viruses, when feeding on plants. Michelle Heck underlined how significant this study is for comprehending the molecular bases of aphid-vector manipulation by plant viruses (see below). Interestingly, the study design has integrated several factors that might influence the gene expression of M. persicae when feeding on the plant. Indeed, the authors investigated the effect of two plant species (Arabidopsis thaliana and Camelia sativa) and two virus species [turnip yellows virus (TuYV) and cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV)]. Noteworthy, the transmission mode of TuYV is circulative and persistent, while CaMV is transmitted by a semi-persistent non-circulative mode. As Juan José Lopez Moya mentioned, multiple comparisons allowed the identification of the different responses of aphids in front of different host plants infected or not by different viruses (see below). This publication is complementary to a previous publication from the same team focusing on plant transcriptome analysis [3]. Thanks to their experimental design, the authors identified genes commonly deregulated by both viruses and/or both plant species and deregulated genes by a single virus or a single plant. Figure 4 nicely summarizes the number of deregulated genes. A thorough discussion on the putative role of deregulated genes in different conditions gave a comprehensive follow-up of the results and their impact on the current knowledge of plant-virus-vector interactions. This study has now opened the gate to promising research focusing on the functional validation of the identified genes while also narrowing the study from the body to the tissue level. References: 1. Carr JP, Tungadi T, Donnelly R, Bravo-Cazar A, Rhee S-J, Watt LG, Mutuku JM, Wamonje FO, Murphy AM, Arinaitwe W, Pate AE, Cunniffe NJ, Gilligan CA (2020) Modelling and manipulation of aphid-mediated spread of non-persistently transmitted viruses. Virus Research, 277, 197845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2019.197845 2. Chesnais Q, Golyaev V, Velt A, Rustenholz C, Verdier M, Brault V, Pooggin MM, Drucker M (2022) Transcriptome responses of the aphid vector Myzus persicae are shaped by identities of the host plant and the virus. bioRxiv , 2022.07.18.500449, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500449 3. Chesnais Q, Golyaev V, Velt A, Rustenholz C, Brault V, Pooggin MM, Drucker M (2022) Comparative Plant Transcriptome Profiling of Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 and Camelina sativa var. Celine Infested with Myzus persicae Aphids Acquiring Circulative and Noncirculative Viruses Reveals Virus- and Plant-Specific Alterations Relevant to Aphid Feeding Behavior and Transmission. Microbiology Spectrum, 10, e00136-22. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.00136-22 | Transcriptome responses of the aphid vector *Myzus persicae* are shaped by identities of the host plant and the virus | Quentin Chesnais, Victor Golyaev, Amandine Velt, Camille Rustenholz, Maxime Verdier, Véronique Brault, Mikhail M. Pooggin, Martin Drucker | <p style="text-align: justify;"><strong>Background:</strong> Numerous studies have documented modifications in vector orientation behavior, settling and feeding behavior, and/or fecundity and survival due to virus infection in host plants. These a... |  | Behaviour of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Cell biology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Molecular biology of infections, Physiology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Phytopathology, Plant diseases, Vectors, Viruses | Sebastien Massart | 2022-07-19 15:24:14 | View | |
23 Jan 2023

Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolenseMoana Peylhard, David Berthier, Guiguigbaza-Kossigan Dayo, Isabelle Chantal, Souleymane Sylla, Sabine Nidelet, Emeric Dubois, Guillaume Martin, Guilhem Sempéré, Laurence Flori, Sophie Thévenon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.10.495622Whole genome transcriptome reveals metabolic and immune susceptibility factors for Trypanosoma congolense infection in West-African livestockRecommended by Concepción Marañón based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersAfrican trypanosomiasis is caused by to the infection of a protozoan parasite of the Trypanosoma genus. It is transmitted by the tsetse fly, and is largely affecting cattle in the sub-humid areas of Africa, causing a high economic impact. However, not all the bovine strains are equally susceptible to the infection (1). In order to dissect the mechanisms underlying susceptibility to African trypanosoma infection, Peylhard et al (2) performed blood transcriptional profiles of trypanotolerant, trypanosensitive and mixed cattle breeds, before and after experimental infection with T. congolense. First of all, the authors have characterized the basal transcriptional profiles in the blood of the different breeds under study, which could be classified in a wide array of functional pathways. Of note, after infection some pathways were consistently enriched in all the group tested. Among them, the immune system-related ones were again on the top functions reported. The search for specific canonical pathways pointed to a prominent role of lipid and cholesterol-related pathways, as well as mitochondrial function and B and T lymphocyte activation. However, the analysis of infected animals demonstrated that trypanosusceptible animals showed a stronger transcriptomic reprogramming, highly enriched in specific metabolic and immunological pathways. It is worthy to highlight striking differences in genes involved in immune signal transduction, cytokines and markers of different leukocyte subpopulations. This work represents undoubtedly a significant momentum in the field, since the authors explore in deep a wide panel of cattle breeds representing the majority of West-African taurine and zebu in a systematic way. Since the animals were studied at different timepoints after infection, future longitudinal analyses of these datasets will be providing a precious insight on the kinetics of immune and metabolic reprogramming associated with susceptibility and tolerance to African trypanosoma infection, widening the application of this interesting study into new therapeutic interventions. References 1. Berthier D, Peylhard M, Dayo G-K, Flori L, Sylla S, Bolly S, Sakande H, Chantal I, Thevenon S (2015) A Comparison of Phenotypic Traits Related to Trypanotolerance in Five West African Cattle Breeds Highlights the Value of Shorthorn Taurine Breeds. PLOS ONE, 10, e0126498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126498 2. Peylhard M, Berthier D, Dayo G-K, Chantal I, Sylla S, Nidelet S, Dubois E, Martin G, Sempéré G, Flori L, Thévenon S (2022) Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolense. bioRxiv, 2022.06.10.495622, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community Infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.10.495622. | Whole blood transcriptome profiles of trypanotolerant and trypanosusceptible cattle highlight a differential modulation of metabolism and immune response during infection by Trypanosoma congolense | Moana Peylhard, David Berthier, Guiguigbaza-Kossigan Dayo, Isabelle Chantal, Souleymane Sylla, Sabine Nidelet, Emeric Dubois, Guillaume Martin, Guilhem Sempéré, Laurence Flori, Sophie Thévenon | <p>Animal African trypanosomosis, caused by blood protozoan parasites transmitted mainly by tsetse flies, represents a major constraint for millions of cattle in sub-Saharan Africa. Exposed cattle include trypanosusceptible indicine breeds, severe... |  | Animal diseases, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Resistance/Virulence/Tolerance | Concepción Marañón | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-06-14 17:06:57 | View |
08 Dec 2022
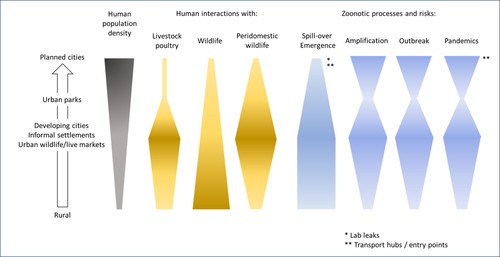
Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystemsDobigny, G. & Morand, S. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776Zoonotic emergence and the overlooked case of citiesRecommended by Etienne Waleckx based on reviews by Eric Dumonteil, Nicole L. Gottdenker and 1 anonymous reviewerZoonotic pathogens, those transmitted from animals to humans, constitute a major public health risk with high associated global economic costs. Diseases associated with these pathogens represent more than 60% of emerging infectious diseases and predominantly originate in wildlife (1). Over the last decades, the emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic pathogens have led to an increasing number of epidemics, as illustrated by the current Covid-19 pandemic. There is ample evidence that human impact on native ecosystems such as deforestation, agricultural development, and urbanization, is linked to spillover of pathogens from animals to humans (2). However, research and calls to action have mainly focused on the importance of surveillance and prevention of zoonotic emergences along landscape interfaces, with special emphasis on tropical forests and agroecosystems, and studies and reviews pointing out the zoonotic risk associated with cities are scarce. Additionally, cities are sometimes wrongly seen as one homogeneous ecosystem, almost exclusively human, with a Northern hemisphere-biased perception of what a city is, which fails to take into account the ecological and socio-economic diversities that can constitute an urban area. Here, Dobigny and Morand (3) aim to draw attention to the importance of urban ecosystems in zoonotic risk and advocate that further attention should be paid to urban, peri-urban and suburban areas. In this well-organized and well-documented review, the authors show, using updated literature, that cities are places where massive contacts occur between wildlife, domestic animals, and human inhabitants (thus constituting spillover opportunities), and that it is even likely that human and wildlife contact in urban centers is more prevalent than in wild areas, perhaps contrary to intuition. Indeed, cities currently constitute the most important environment of human life and are places for millions of close interactions between humans and animals, including pets and domestic animals, wild animals through the intrusion of wild urban-adapted species (e.g., some bat, rodent, or bird species among others), manipulation and consumption of wildlife meat, and the existence of wildlife meat markets, which all constitute a major risk for zoonotic spillover. In cities, lab escapees of zoonotic pathogens also exist, and trends of adaptation to urban ecological conditions of many vectors of primary health importance is also a concern. The authors further argue that cities are predominant places for both epidemic amplification of human-human transmitted pathogens, because they are places with high human densities and population growth, and for dissemination of reservoirs, vectors and pathogens, as they are transport hubs. Dobigny & Morand further predict, likely correctly, that cities may be important places for pathogen evolution. Finally, they propose actions and recommendations to limit the risk of zoonotic spillover events from urban ecosystems and future directions for research aiming at assessing this risk. The reviewers found the manuscript well-organized and presented, timely, and bringing novel contributions to the field of zoonotic emergence. I strongly recommend this article, which should benefit a large audience, particularly in the context of the current Covid-19 pandemics and the ongoing One Health initiatives aiming at preventing future zoonotic disease emergence (4). References (1) Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature, 451, 990–993. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06536 (2) White RJ, Razgour O (2020) Emerging zoonotic diseases originating in mammals: a systematic review of effects of anthropogenic land-use change. Mammal Review, 50, 336–352. https://doi.org/10.1111/mam.12201 (3) Dobigny G, Morand S (2022) Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems. Zenodo, 6444776, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6444776 (4) Morand S, Lajaunie C (2021) Biodiversity and COVID-19: A report and a long road ahead to avoid another pandemic. One Earth, 4, 920–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2021.06.007 | Zoonotic emergence at the animal-environment-human interface: the forgotten urban socio-ecosystems | Dobigny, G. & Morand, S. | <p style="text-align: justify;">Zoonotic emergence requires spillover from animals to humans, hence animal-human interactions. A lot has been emphasized on human intrusion into wild habitats (e.g., deforestation, hunting) and the development of ag... |  | Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecohealth, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, One Health, Zoonoses | Etienne Waleckx | 2022-04-11 11:39:11 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Jorge Amich
Christine Chevillon
Fabrice Courtin
Christine Coustau
Thierry De Meeûs
Heather R. Jordan
Karl-Heinz Kogel
Yannick Moret
Thomas Pollet
Benjamin Roche
Benjamin Rosenthal
Bashir Salim
Lucy Weinert










