
BOJKO Jamie
- School of Health and Life Sciences, Teesside University and National Horizons Centre, Darlington, United Kingdom
- Animal diseases, Behaviour of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Disease Ecology/Evolution, Ecology of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Eukaryotic pathogens/symbionts, Evolution of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Genomics, functional genomics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Infections and conservation biology (of plants, or animals), Molecular genetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Parasites, Pathogenic/Symbiotic Bacteria, Pathogenic/Symbiotic Fungi, Phylogenetics of hosts, infectious agents, or vectors, Viruses, Zoonoses
- recommender
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
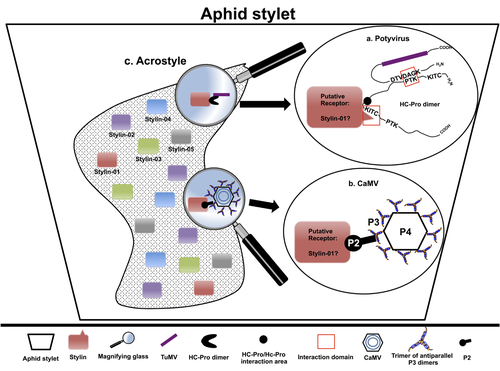
The helper strategy in vector-transmission of plant viruses
The intriguing success of helper components in vector-transmission of plant viruses.
Recommended by Christine Coustau based on reviews by Jamie Bojko and Olivier SchumppMost plant-infecting viruses rely on an animal vector to be transmitted from one sessile host plant to another. A fascinating aspect of virus-vector interactions is the fact that viruses from different clades produce different proteins to bind vector receptors (1). Two major processes are described. In the “capsid strategy”, a motif of the capsid protein is directly binding to the vector receptor. In the “helper strategy”, a non-structural component, the helper component (HC), establishes a bridge between the virus particle and the vector’s receptor.
In this exhaustive review focusing on hemipteran insect vectors, Di Mattia et al. (2) are revisiting the helper strategy in light of recent results. The authors first place the discoveries of the HC strategy in a historical context, suggesting that HC are exclusively found in non-circulative viruses (viruses that only attach to the vector). They present an overview of the nature and modes of action of helper components in the major virus clades of non-circulative viruses (Potyviruses and Caulimoviruses). Authors then detail recent advances, to which they have significantly contributed, showing that the helper strategy also appears widespread in circulative transmission categories (Tenuiviruses, Nanoviruses).
In an extensive perspective section, they raise the question of the evolutionary significance of the existence of HC in numerous unrelated viruses, transmitted by unrelated vectors through different mechanisms. They explore the hypothesis that the helper strategy evolved several times independently in distinct viral clades and for different reasons. In particular, they present several potential benefits of plant virus HC related to virus cooperation, collective transmission and effector-driven infectivity.
As pointed out by both reviewers, this is a very clear and synthetic review. Di Mattia et al. present an exhaustive overview of virus HC-vector molecular interactions and address functionally and evolutionarily important questions. This review should benefit a large audience interested in host-virus interactions and transmission processes.
REFERENCES
(1) Ng JCK, Falk BW (2006) Virus-Vector Interactions Mediating Nonpersistent and Semipersistent Transmission of Plant Viruses. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 44, 183–212. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.070505.143325
(2) Di Mattia J, Zeddam J-L, Uzest M, Blanc S (2023) The helper strategy in vector-transmission of plant viruses. Zenodo, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Infections. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7709290